Berkelium (III) fluoride
| Crystal structure | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
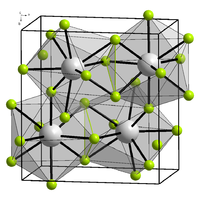
|
|||||||
| __ Bk 3+ __ F - | |||||||
| Crystal system | |||||||
| Lattice parameters |
a = 670 pm |
||||||
| Coordination numbers |
Bk [9], F [3] |
||||||
| General | |||||||
| Surname | Berkelium (III) fluoride | ||||||
| other names |
Berkelium trifluoride |
||||||
| Ratio formula | BkF 3 | ||||||
| Brief description |
yellow-green solid |
||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||
|
|||||||
| properties | |||||||
| Molar mass | 304.07 g mol −1 | ||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||
| density |
9.70 g cm −3 |
||||||
| Hazard and safety information | |||||||
 Radioactive |
|||||||
|
|||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||
Berkelium (III) fluoride is a chemical compound consisting of the elements berkelium and fluorine . It has the formula BkF 3 and belongs to the fluoride class of substances .
properties
Berkelium (III) fluoride is a yellow-green solid and has two crystalline structures that are temperature-dependent. At low temperatures the orthorhombic structure ( YF 3 -type) can be found with a = 670 pm , b = 709 pm and c = 441 pm as well as a density of 9.70 g cm −3 . At higher temperatures it forms a trigonal system ( LaF 3 type) with a = 697 pm and c = 714 pm and a density of 10.15 g · cm −3 . Each berkelium nucleus is surrounded by nine fluorine nuclei in a distorted triple-capped trigonal-prismatic structure. The transition temperature of BkF 3 is in the range from 350 to 600 ° C.
use
The first samples of berkelium metal were produced in 1969 by reducing BkF 3 at 1000 ° C with lithium in tantalum reaction apparatus .
safety instructions
Classifications according to the CLP regulation are not available because they only include chemical hazard and play a completely subordinate role compared to the hazards based on radioactivity . The latter also only applies if the amount of substance involved is relevant.
Individual evidence
- ↑ Berkelium (III) fluoride at www.webelements.com.
- ^ A b J. R. Peterson, BB Cunningham: Crystal Structures and Lattice Parameters of the Compounds of Berkelium IV. Berkelium Trifluoride , in: J. Inorg. Nucl. Chem. , 1968 , 30 (7), pp. 1775-1784 ( doi : 10.1016 / 0022-1902 (68) 80353-7 ).
- ↑ The hazards emanating from radioactivity do not belong to the properties to be classified according to the GHS labeling. With regard to other hazards, this substance has either not yet been classified or a reliable and citable source has not yet been found.
- ↑ DD Ensor, JR Peterson, RG Haire, JP Young: Absorption Spectrophotometric Study of Berkelium (III) and (IV) Fluorides in the Solid State , in: J. Inorg. Nucl. Chem. , 1981 , 43 (5), pp. 1001-1003 ( doi : 10.1016 / 0022-1902 (81) 80164-9 ).
- ↑ Joseph Richard Peterson: The Solution Absorption Spectrum of Bk 3+ and the Crystallography of Berkelium Dioxide, Sesquioxide, Trichloride, Oxychloride, and Trifluoride , Ph.D. Thesis, October 1967, US Atomic Energy Commission Document Number UCRL-17875 (1967).
- ↑ JR Peterson, JA Fahey, RD Baybarz: The Crystal Structures and Lattice Parameters of Berkelium Metal , in: J. Inorg. Nucl. Chem. , 1971 , 33 (10), pp. 3345-3351 ( doi : 10.1016 / 0022-1902 (71) 80656-5 ).
literature
- David E. Hobart, Joseph R. Peterson: Berkelium , in: Lester R. Morss, Norman M. Edelstein, Jean Fuger (Eds.): The Chemistry of the Actinide and Transactinide Elements , Springer, Dordrecht 2006; ISBN 1-4020-3555-1 , pp. 1444-1498 ( doi : 10.1007 / 1-4020-3598-5_10 ).
