Lanthanum fluoride
| Crystal structure | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||||||||||||
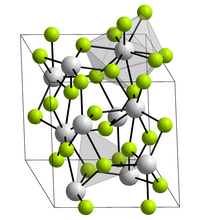
| __ La 3+ __ F - | ||||||||||||||||
| Crystal system | ||||||||||||||||
| Space group |
P 3 c 1 (No. 165) |
|||||||||||||||
| Lattice parameters |
a = 719 pm |
|||||||||||||||
| Coordination numbers |
La [9], F [3] |
|||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Lanthanum fluoride | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Ratio formula | LaF 3 | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
white, odorless solid |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 195.90 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
5.9 g cm −3 |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
1493 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
2327 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
almost insoluble in water, soluble in strong mineral acids |
|||||||||||||||
| Refractive index |
1.59 |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . Refractive index: Na-D line , 20 ° C | ||||||||||||||||
Lanthanum fluoride is a chemical compound from the group of fluorides .
Occurrence
Lanthanum fluoride occurs naturally as the mineral fluocerite- (La) , which contains cerium in addition to lanthanum . The cerium-rich lanthanum fluoride mineral is also called tysonite after the American naturalist ST Tyson.
Extraction and presentation
Lanthanum fluoride can be obtained by reacting hydrogen fluoride with lanthanum nitrate or lanthanum chloride.
The reaction of lanthanum oxide with ammonium hydrogen difluoride is also possible.
properties
Lanthanum fluoride crystallizes trigonally in the space group P 3 c 1 (space group no. 165) with the lattice parameters a = 719 pm and c = 735 pm and six formula units per unit cell . Each lanthanum atom in the crystal structure is surrounded by nine fluoride ions in the form of a distorted, triple-capped trigonal prism, while the fluorine atoms are each coordinated in a trigonal-planar manner by three lanthanum atoms.
Lanthanum fluoride has an ionic conductivity at elevated temperatures that is based on the mobility of fluoride ions moving in the fluoride vacancies of Schottky defects . If the lanthanum fluoride is doped with the fluoride of a divalent metal, e.g. B. Ca 2+ , Ba 2+ or Eu 2+ , the ionic conductivity can reach considerable values even at room temperature (see also use ).
Lanthanum fluoride is insoluble in water, hydrochloric acid and nitric acid ; it dissolves in concentrated sulfuric acid with the formation of hydrogen fluoride HF.
use
Lanthanum fluoride is used to produce the pure metal lanthanum . For this purpose, the lanthanum oxide found in lanthanum minerals is converted into lanthanum fluoride using hydrogen fluoride, which is then metallothermally reduced to metal using calcium or magnesium . Lanthanum fluoride is also used as an optical material, e.g. B. used for fiber optics or for fluorescent lamps. Doped with europium , LaF 3 serves as a fluoride-permeable membrane ( solid electrolyte ) in fluoride electrodes for the detection of fluoride ions.
Web links
- The Mobility of Ions in Lanthanum Fluoride Nanoclusters
- TRANSPARENT LANTHANUM FLUORIDE GLASS-CERAMICS (WIPO)
- WW Moses, SE Derenzo: The Scintillation Properties of Cerium-Doped Lanthanum Fluoride. In: Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A: Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment, Vol. 299, Vol. 1–3, December 20, 1990, pp. 51–56 doi : 10.1016 / 0168-9002 (90) 90746-S .
Individual evidence
- ↑ Lanthanum fluoride data sheet from AlfaAesar, accessed on April 2, 2010 ( PDF )(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ a b c d Lanthanum Fluoride at American Elements
- ↑ lanthanum at Nivotechnology
- ↑ Lanthanum (III) fluoride data sheet from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on May 6, 2017 ( PDF ).
- ^ Oscar D. Allen, WJ Comstock: Bastnaesite and tysonite from Colorado . In: American Journal of Science . tape 19 , no. 113 , May 1880, p. 390-393 , doi : 10.2475 / ajs.s3-19.113.390 .
- ↑ a b Streng: New Yearbook for Mineralogy, Geology and Paleontology . II. Volume. Schweizerbart'sche Verlagshandlung (E. Koch), Stuttgart 1881, p. 174 ( online on the pages of The Internet Archive ).
- ↑ A. Zalkin, DH Templeton: Refinement of the trigonal crystal structure of lanthanum trifluoride with neutron diffraction data. In: Acta Crystallographica , B 41, 1989, pp. 91-93; doi : 10.1107 / S0108768185001689 .
- ↑ David R. Lide (Ed.): CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics . 87th edition. (Internet version: 2006–2007), CRC Press / Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton, FL, Fluid Properties, pp. 6-113 ( limited preview in Google Book Search).
- ^ William L. Fielder: Ionic Conductivity of Lanthanum Fluoride . Ed .: National Aeronautics and Space Administration NASA. 1969 ( nasa.gov [PDF]).
- ↑ azom.com: Lanthanum Fluoride

