Blue screen (Windows)
A blue screen (even blue screen , rare blue screen ; literally Blue Screen , Microsoft (up to Windows 8 ) officially Bugcheck called), also jokingly Blue Screen of Death (Blue Screen of Death, also briefly BSoD ) or Blue Death (following the Black death ), is a description of a specific category of error messages ( stop errors ), in particular in Microsoft Windows - operating systems are displayed. After a critical system error, the system is stopped and the user interface of the operating system is completely replaced by a blue screen on which the error information appears in white letters.
In most cases, these messages are not triggered by errors in application programs , but by errors in device drivers or in the hardware . If the blue screen is not triggered by a defect in the hardware, it is either a programming error in a driver, in the kernel, which can often be fixed by a patch from the relevant manufacturer, or a faulty system configuration. In certain cases, there may be an underlying error in the software architecture that remains until the end of the product's service life.
In other operating systems, such errors are referred to as kernel panic .
concept
Device and other hardware drivers run in a privileged mode ( kernel mode ), with direct access to system memory areas and hardware interfaces. If a faulty device driver writes data to a memory area that is used by other system parts (including other device drivers), the system integrity is violated. If the system continued to run in such cases, there would be a risk of irreversible data destruction (for example on the hard drive ). The system is therefore stopped immediately and can no longer be operated, which in turn can also have a detrimental effect on the data integrity; in particular, unsaved user data is lost. The system will also halt if a hardware problem occurs that cannot be ignored. This includes, for example, the failure of the system's primary hard drive when attempting to read data from the paging file .
With other operating systems (such as Unix ) this corresponds to the so-called kernel panic .
With modern motherboards (see also ATX ), overheating of the processor can lead to a blue screen, as the temperature control sets the processor to HALT mode.
In the Windows 9x versions , these messages are unsuitable for solving problems, as hardly any information is given to the user:
- The Windows 9x blue screen shows which interrupt triggered by the processor caused a further error during error handling (double error, interrupt 8 ).
- 00 ( Interrupt 0 ): Division by Zero ( division by zero )
- 06 ( Interrupt 6 ): Invalid Opcode ( Invalid command )
- 0D ( Interrupt 13 ): General Protection Fault ( General Protection Fault )
- 0E ( Interrupt 14 ): Paging Fault ( page fault )
In addition, two addresses and, in some cases, the file concerned are also output.
In the Internet , particularly in the Microsoft Knowledge Base , many combinations of are error codes and addresses, as well as possible causes described.
With the introduction of Windows NT 4.0, an error number and error description are displayed as well as four numerical values, with the help of which experienced and knowledgeable users can identify the causes of errors with the help of the Microsoft website. Windows can also be configured in such a way that the content of the main memory is written to the hard drive as a kernel , small or complete memory dump for subsequent analysis ( core dump ), if this is still possible.
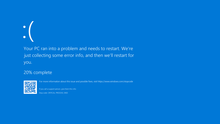
Starting with Windows 8, the blue screen has been simplified, a sad face appears on the screen, under it it says that an error has occurred and that information is collected about how advanced this is is described in percentages. Below is an error code, but without a stop code. By default, a restart will be performed once the information has been collected. In newer versions of Windows 10, Microsoft offers to scan a QR code in order to be redirected to the website with the solutions.
With MS-DOS- based Windows versions this message often requires a restart of the system, with Windows NT-based versions it always needs to be restarted. In the Home versions of Windows XP ( Service Pack 1 and 2), the required manual restarts in was standard - configuration replaced by an automatic restart; However, in critical situations, this can lead to deadlock ( deadlock cause the system): The computer crashes with blue screen off automatically restarts and crashes immediately again. The remedy in such cases is to select the option “Deactivate automatic restart in the event of a system error” in the boot manager menu and possibly start the computer in safe mode , which prevents the aforementioned, often almost immediate, restart.
Blue screen at a performance
Perhaps the most famous occurrence of Windows 9x blue screen came during a presentation of Windows 98 beta by Bill Gates at COMDEX on April 20, 1998: The demonstration computer crashed with a blue screen off when Gates's assistant Chris Capossela a scanner with connected to the PC to demonstrate plug and play device support in Windows 98. The event brought thunderous applause from the audience, and after a nervous pause, Gates replied, “ That must be why we're not shipping Windows 98 yet. “(That is probably the reason why we don't ship Windows 98 yet.)
Error messages in other colors
The Windows 8 Black Screen of Death
In some beta versions of Windows 8 the blue screen with a black screen (black screen replaced). Nevertheless, a blue screen appears in the official versions of Windows 8, but it looks a bit more modern than the previous versions.
The MS-DOS 6 Black Screen of Death
MS-DOS 6 is the oldest Microsoft operating system that has the blue screen, but it is displayed in the color set for the BIOS screen driver (usually light gray on black). It is displayed by the EMM386.EXE driver - which corresponds to the Windows or Linux kernel - if an untreated processor interrupt (e.g. Segfault, Division by Zero) occurs in protected mode . In the same situation, MS-DOS 5 displays a critical error and the user is left with the option to exit Protected Mode and return to the DOS command line interpreter , while MS-DOS 6 displays the "real" blue screen with only the restart is still possible.
The Windows 3.1 Black Screen of Death
In Microsoft Windows 3.x , the Black Screen of Death appears if an MS-DOS application could not be executed correctly. Very often this occurs when certain functions are performed while the network driver in memory is active. For instance, while loading the Novell - Netware clients NETX for MS-DOS: The system attempts when the error occurred in the text mode to change, but does not show anything, so that the user sits in front of a blank black screen, left on in the a cursor flashes in the upper corner . At this point, the user can no longer make any entries and is forced to cold start the system in order to continue working.
According to Wallace McClure of ASP.net printed the Black Screen of Death for the first time in the summer of 1991 by Ed Brown, an IT technician Coca-Cola Company in Atlanta used, who reported that the company's employees while trying to WordPerfect to start, got a black screen of death every now and then .
The Xbox 360 black screen
On Xbox 360 , if a general error occurs, a black screen appears and the console can no longer be used. The black screen says you should contact Xbox support. An error code (e.g. E71, E64 ...) is also displayed. The circle on which the number of connected controllers is normally displayed lights up a quarter red, similar to the Red Ring of Death .
The OS / 2 Black Screen of Death
In OS / 2 , a black screen of death is either a TRAP screen or a full-screen hard-error VIO pop-up. Both ensure that the ad is switched to text mode . This display has 25 lines with 80 columns each to display the text, in which white letters are displayed on a black background, which is where this display got its name from.
TRAP screen
A TRAP screen is displayed if an error occurs in the kernel that cannot be corrected at runtime . Usually this happens after the overclocking of hardware , but also software problems with the kernel or device drivers .
The TRAP screen thereby contains both a list of the processor - register and stack as well as information about the version of the operating system and the error that occurred in the processor.
The only option available to the user in this situation is either to restart the system using the clip handle (pressing Strg+ Alt+ at the same time Entf) or by pressing Strg+ Alt+ twice Num Lockto instruct the system to save all information from memory to disk .
Hard error screen
A full-screen hard-error VIO pop-up is displayed when a process causes a fatal error, either a program crash or a fatal error where it is possible to restore the system, e.g. B. triggered by an attempt to read a floppy disk , although none is in the floppy disk drive .
This display is generated by the hard error daemon process, which handles serious errors from other processes. Technically, this ad is a VIO pop-up ad. All processes (except the one that triggered the fatal error) continue to run. This daemon uses a VIO pop-up when either the system is started in text mode or when the error occurs in a process running in full screen mode.
This pop-up contains information about the error that occurred and the process that triggered it.
The user is then asked how to proceed. He can choose between the following actions:
- End process,
- Display more information (list of processor - register and stack )
- Repetition of the action leading to the error (if possible - e.g. I / O errors can be repeated, CPU errors cannot) or
- Ignoring the error (if possible - for example I / O errors can be ignored, CPU errors cannot).
Red Screen of Death
The Red Screen of Death (RSoD) is a variant that was present in some beta versions of the Windows Vista operating system .
Fatal errors in newer versions of Lotus Notes are also referred to as the Red Screen of Death . An error message appears there, but not as with Windows Vista in full screen mode, but as a red box with a black frame.
Other uses
- The red screen is also used by some flight simulators (such as those from FlightSafety International). As soon as a pilot crashes the plane, every screen in the cockpit turns red.
- With the PlayStation 2 , this is also used to support the following error message: “Insert DVD / CD-ROM in PlayStation or PlayStation 2 format”. This error is caused by an unsupported or unreadable disc.
- In the case of the PlayStation Portable , RSoD occurs very rarely when the flash0 (the internal flash disk) is damaged.
- On the SEGA Genesis / Mega Drive, incorrectly patched ROMs acknowledge their service with a red screen that does not contain any text. The console must be reset in this case.
Error messages in iOS
The iPhone 5s also shows a blank blue screen as a result of a system crash and then reboots the device. One possible cause on the software side is the synchronization of Apple's own iWork apps Pages, Numbers or Keynote. Incorrect installation of a replacement display can also trigger the error.
See also
Individual evidence
- ↑ COMDEX BSoD . CNNi. 1998. Retrieved December 13, 2010.
- ↑ Origin of BSOD - Wallace B. McClure
- ↑ iPhone 5S users report Blue Screen Of Death reboots
- ↑ More app crashes than the iPhone 5: Apps trip over A7 processor.
- ↑ iPhone 5s blue screen
Web links
- Explanation of each error code - Microsoft website that lists the possible causes for each error; useful for fault diagnosis
- Windows Help Page: Stop Error - extensive troubleshooting for blue screens