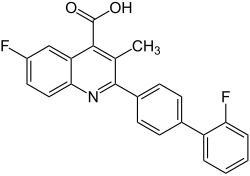
Brequinar
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Brequinar | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 23 H 14 F 2 NO 2 • Na • xH 2 O | |||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 397.35 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Brequinar is a chemical compound from the group of biphenyl quinolines .
properties
Brequinar was developed in the 1980s and is a selective inhibitor of dihydroorotate dehydrogenase in the mitochondria and thus inhibits the biosynthesis of pyrimidine - nucleotides and subsequent biosynthesis as that of nucleic acids . As a result, cell growth is inhibited. In addition, interferon- inducible genes are increasingly expressed . Further inhibitors of dihydroorotate dehydrogenase are teriflunomide and leflunomide .
Brequinar was investigated as a potential chemotherapeutic agent and as an immunosuppressive agent to avoid rejection reactions after organ transplantation , but did not reach phase III due to its low efficacy, therapeutic window and severe side effects in the event of overdose . The main side effect is myelosuppression , with an inhibition of the production of interleukin-1 and tumor necrosis factor α and an inhibition of the activation of T cells . Brequinar was in some types of cancer , for use in a combination therapy studied, and as antiparasitic and antiviral agent . In cell culture brequinar inhibits viral replication of dengue virus , West Nile virus , yellow fever virus , Lassa virus , Junin virus , lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus , Vesicular stomatitis Indiana virus , HIV-1 , Powassan virus and foot-and-mouth disease virus .
Analytics
The reliable qualitative and quantitative determination of brequinar is possible after appropriate sample preparation by HPLC with UV detection at 254 nm.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b Sigma-Aldrich: Brequinar sodium salt hydrate, ≥97% (HPLC)
- ↑ a b c d G. J. Peters: Re-evaluation of Brequinar sodium, a dihydroorotate dehydrogenase inhibitor. In: Nucleosides, nucleotides & nucleic acids. Volume 37, number 12, 2018, pp. 666-678, doi : 10.1080 / 15257770.2018.1508692 (free full text), PMID 30663496 .
- ↑ M. Lucas-Hourani, D. Dauzonne, P. Jorda, G. Cousin, A. Lupan, O. Helynck, G. Caignard, G. Janvier, G. André-Leroux, S. Khiar, N. Escriou, P. Desprès, Y. Jacob, H. Munier-Lehmann, F. Tangy, PO Vidalain: Inhibition of pyrimidine biosynthesis pathway suppresses viral growth through innate immunity. In: PLoS pathogens. Volume 9, number 10, 2013, p. E1003678, doi : 10.1371 / journal.ppat.1003678 , PMID 24098125 , PMC 3789760 (free full text).
- ↑ DV Cramer: brequinar sodium. In: Pediatric nephrology. Volume 9 Suppl, 1995, pp. S52-S55, doi : 10.1007 / bf00867685 , PMID 7492488 .
- ↑ X. Xu, JW Williams, J. Shen, H. Gong, DP Yin, L. Blinder, RT Elder, H. Sankary, A. Finnegan, AS Chong: In vitro and in vivo mechanisms of action of the antiproliferative and immunosuppressive agent, brequinar sodium. In: Journal of immunology. Volume 160, Number 2, January 1998, pp. 846-853, PMID 9551920 .
- ↑ Vyas, M. Ghate: Recent developments in the medicinal chemistry and therapeutic potential of dihydroorotate dehydrogenase (DHODH) inhibitors. In: Mini reviews in medicinal chemistry. Volume 11, Number 12, October 2011, pp. 1039-1055, doi : 10.2174 / 138955711797247707 , PMID 21861807 .
- ↑ JT Madak, A. Bankhead, CR Cuthbertson, HD Showalter, N. Neamati: Revisiting the role of dihydroorotate dehydrogenase as a therapeutic target for cancer. In: Pharmacology & therapeutics. Volume 195, 03 2019, pp. 111-131, doi : 10.1016 / j.pharmthera.2018.10.012 , PMID 30347213 .
- ↑ D. Boschi, AC Pippione, S. Sainas, ML Lolli: Dihydroorotate dehydrogenase inhibitors in anti-infective drug research. In: European journal of medicinal chemistry. Volume 183, December 2019, p. 111681, doi : 10.1016 / j.ejmech.2019.111681 , PMID 31557612 .
- ↑ SF Li, MJ Gong, YF Sun, JJ Shao, YG Zhang, HY Chang: Antiviral activity of brequinar against foot-and-mouth disease virus infection in vitro and in vivo. In: Biomedicine & pharmacotherapy = Biomedecine & pharmacotherapy. Volume 116, August 2019, p. 108982, doi : 10.1016 / j.biopha.2019.108982 , PMID 31146110 .
- ↑ a b c d e f g h i j PI Andersen, K. Krpina, A. Ianevski, N. Shtaida, E. Jo, J. Yang, S. Koit, T. Tenson, V. Hukkanen, MW Anthonsen, M Bjoras, M. Evander, MP Windisch, E. Zusinaite, DE Kainov: Novel Antiviral Activities of Obatoclax, Emetine, Niclosamide, Brequinar, and Homoharringtonine. In: Viruses. Volume 11, number 10, October 2019, p., Doi : 10.3390 / v11100964 , PMID 31635418 , PMC 6832696 (free full text).
- ↑ JG Park, G. Ávila-Pérez, A. Nogales, P. Blanco-Lobo, JC de la Torre, L. Martínez-Sobrido: Identification and Characterization of Novel Compounds with Broad-Spectrum Antiviral Activity against Influenza A and B Viruses. In: Journal of Virology . Volume 94, number 7, March 2020, p., Doi : 10.1128 / JVI.02149-19 , PMID 31941776 , PMC 7081893 (free full text).
- ↑ SF Li, MJ Gong, YF Sun, JJ Shao, YG Zhang, HY Chang: Antiviral activity of brequinar against foot-and-mouth disease virus infection in vitro and in vivo. In: Biomedicine & pharmacotherapy = Biomedecine & pharmacotherapy. Volume 116, August 2019, p. 108982, doi : 10.1016 / j.biopha.2019.108982 , PMID 31146110 .
- ↑ Dasgupta S, Timby DM, Lam GN: Determination of brequinar in rat plasma by direct deproteinization and reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography with ultraviolet absorbance detection. , J Chromatogr B Biomed Appl. 1995 Nov 3; 673 (1): 107-12, PMID 8925063