Cadmium arsenide
| Crystal structure | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
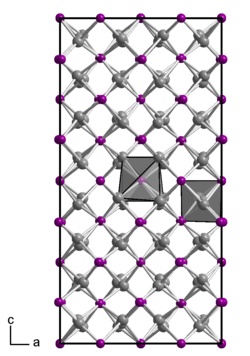
|
||||||||||||||||
| __ Cd 2+ __ As 3− | ||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Cadmium arsenide | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
Tricadmium diarsenide |
|||||||||||||||
| Ratio formula | Cd 3 As 2 | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
dark gray odorless solid |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 487.04 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
3.031 g cm −3 |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
621 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Cadmium arsenide is an inorganic chemical compound of cadmium from the group of arsenides .
Extraction and presentation
Cadmium arsenide can be produced by reacting cadmium with a hydrogen stream laden with arsenic vapor .
properties
Cadmium arsenide is a dark gray odorless solid which has a tetragonal crystal structure with the space group I 4 1 / acd (space group no. 142) and the lattice parameters a = 1267 pm and c = 2548 pm. The structure is very complex and consists of 32 formula units in the unit cell . They can be described as being made up of chains of Cd atoms and As atoms, each Cd atom being tetrahedrally surrounded by four As atoms and each As atom by six Cd atoms, creating a three-dimensional network. However, there are also other modifications, such as a phase transition at 615 ° C. The cadmium diarsenide CdAs 2 , which also exists, is a gray solid that can be obtained by melting cadmium and arsenic at 650 ° C in a vacuum . It has a tetragonal crystal structure with the space group I 4 1 22 (No. 98) .
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f data sheet cadmium arsenide from AlfaAesar, accessed on April 24, 2014 ( PDF )(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ Not explicitly listed in Regulation (EC) No. 1272/2008 (CLP) , but with the indicated labeling it falls under the group entries on cadmium compounds, with the exception of cadmium sulphoselenide (xCdS.yCdSe), reaction mass of cadmium sulphide with zinc sulphide (xCdS.yZnS), reaction mass of cadmium sulphide with mercury sulphide (xCdS.yHgS), and those specified elsewhere in this Annex and arsenic acid and its salts with the exception of those specified elsewhere in this Annex in the Classification and Labeling Inventory of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), accessed on March 18, 2017. Manufacturers or distributors can expand the harmonized classification and labeling .
- ↑ a b c Georg Brauer , with the assistance of Marianne Baudler a . a. (Ed.): Handbook of Preparative Inorganic Chemistry . 3rd, revised edition. tape I . Ferdinand Enke, Stuttgart 1975, ISBN 3-432-02328-6 , pp. 1047 .
- ^ MN Ali, Q. Gibson, S. Jeon, BB Zhou, A. Yazdani, RJ Cava: The Crystal and Electronic Structures of Cd3As2, the Three-Dimensional Electronic Analogue of Graphene. In: Inorganic Chemistry , 53, 2014, pp. 4062-4067, doi: 10.1021 / ic403163d .
- ↑ SER Hiscocks, CT Elliott: On the preparation, growth and properties of Cd3As2. In: Journal of Materials Science. 4, 1969, pp. 784-788, doi : 10.1007 / BF00551073 .
- ↑ W. Frey country A. Goltzene, P. Grosse, G. Harbeke, H. Lehmann, O. Madelung, W. Richter, C. Schwab, G. Weiser, H. Werheit, W. Zdanowicz: Physics of Non-tetrahedrally Bonded elements and Binary compounds I / Physics of non-tetrahedral-linked elements and binary compounds I . Springer, 1983, ISBN 3-540-11780-6 , pp. 203 ( limited preview in Google Book search).



