Calcium adipate
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
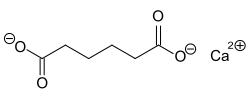
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Calcium adipate | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
Calcium hexanedioate |
||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 6 H 8 CaO 4 | ||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 184.20 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
40.2 g l −1 (13 ° C) |
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||||||||
Calcium adipate is a chemical compound from the group of carboxylic acid salts and the calcium salt of adipic acid .
Manufacturing
Calcium adipate can be made by precipitating a hot calcium chloride solution with sodium adipate .
The neutralization of a calcium hydroxide solution with adipic acid also provides calcium adipate.
properties
Calcium adipate crystallizes as monohydrate in the triclinic crystal system in space group P 1 (space group no. 1) with the lattice parameters a = 589.9 pm , b = 679.8 pm, c = 1082.1 pm, α = 78.999 °, β = 81.831 ° and γ = 82.971 °. In the unit cell contains two formula units . It is much more soluble in cold water than in hot water - at 12 ° C 40.2 g dissolves in 1 liter of water, at 100 ° C only 12.0 g.
The pyrolysis of calcium adipate at 350 ° C yields cyclopentanone and calcium carbonate .
The standard free enthalpy of formation of calcium adipate is Δ f G 0 = -1214.405 kJ / mol.
use
Calcium adipate has been suggested as an additive in cigarettes to reduce the amount of menthol added due to taste . It has also been suggested as an additive in toothpastes .
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d W. Dieterle, C. Hell: "To the knowledge of adipic acid" in Ber. d. German chem. Ges. 1884 , 17 , pp. 2221-2228. Full text
- ↑ This substance has either not yet been classified with regard to its hazardousness or a reliable and citable source has not yet been found.
- ↑ M. Mathew, S. Takagi, HL Ammon: "Crystal structure of calcium adipate monohydrate" in Journal of Chemical Crystallography 1993 , 23 (8), pp. 617-621. doi : 10.1007 / BF01325183
- ^ Raj K. Bansal: "A text book of organic chemistry", New Age International Verlag, 4th edition, ISBN 9788122414592 , p. 475 ( limited preview in the Google book search).
- ↑ Dissertation: "Experimental investigation and modeling of the solubility of limestone and gypsum in aqueous systems at higher ionic strengths", Dieter Loos, 2003, University of Duisburg-Essen. Full text (PDF; 1.2 MB)
- ↑ Patent US3082125 . full text
- ↑ patent US4460565 . full text


