Carthamin
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
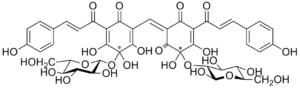
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Carthamin | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 43 H 42 O 22 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
red solid |
||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 910.78 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
228-230 ° C |
||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
Slightly soluble in water, soluble in ethanol and dilute alkali metal carbonate solution |
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||||||||
Carthamin is the yellowish-red natural dye from the petals of safflower , which also Saf (f) lor is called.
Extraction
Since the dye is water-soluble, it can be removed by washing it out of the safflower petals, then dried and obtained as safflower red in an alkaline solution .
properties
The dye is only moderately soluble in water and not particularly lightfast .
use
Wool , cotton and silk can be dyed pink, cherry-red, brown-red or brown-yellow, depending on the amount of dye used. Carthamin is also used as the Natural Red 26 food coloring .
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d Entry on Carthamin. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on November 12, 2014.
- ↑ This substance has either not yet been classified with regard to its hazardousness or a reliable and citable source has not yet been found.
- ↑ Carthamin . In: Merck's Warenlexikon . 3rd ed. 1884 ff., P. 73 f.
- ↑ Handbook of Chemistry, Volume 7 . 1866, p. 1193 ( limited preview in Google Book Search).
Web links
- Entry on safflower in Meyers Konversationslexikon
- Safflower . In: Merck's Warenlexikon . 3rd ed. 1884 ff., P. 472 f.
