Chlorobenzoic acids
| Chlorobenzoic acids | ||||||
| Surname | 2-chlorobenzoic acid | 3-chlorobenzoic acid | 4-chlorobenzoic acid | |||
| other names | o -chlorobenzoic acid | m -chlorobenzoic acid | p -chlorobenzoic acid | |||
| Structural formula |
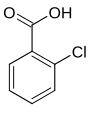
|

|
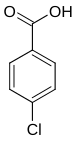
|
|||
| CAS number | 118-91-2 | 535-80-8 | 74-11-3 | |||
| PubChem | 8374 | 447 | 6318 | |||
| Molecular formula | C 7 H 5 ClO 2 | |||||
| Molar mass | 156.57 g mol −1 | |||||
| Physical state | firmly | |||||
| Brief description | colorless powder | beige crystalline powder | white crystalline powder | |||
| Melting point | 139-142 ° C | 153-156 ° C | 237-240 ° C | |||
| boiling point | 285 ° C | 274-276 ° C | 274-276 ° C | |||
| pK s value | 2.92 | 3.82 | 3.98 | |||
| solubility | 2.1 g / l (25 ° C) | 0.45 g / l (20 ° C) | 0.08 g / l (20 ° C) | |||
|
GHS labeling |
|
|
|
|||
| H and P phrases | 315-319 | 315-319 | 302-315-319-335 | |||
| no EUH phrases | no EUH phrases | no EUH phrases | ||||
| 302 + 352-305 + 351 + 338 | 302 + 352-305 + 351 + 338 | 261-305 + 351 + 338 | ||||
In chemistry, chlorobenzoic acids form a group of substances that are derived from both benzoic acid and chlorobenzene . The structure consists of a benzene ring with an attached carboxy group (–COOH) and chlorine (–Cl) as substituents . Their different arrangement results in three constitutional isomers with the empirical formula C 7 H 5 ClO 2 .
presentation
4-Chlorobenzoic acid is produced from 4-chlorotoluene by oxidation of the methyl group with potassium permanganate in alkaline solution (in the presence of a phase transfer catalyst ). The preparation of 2-chlorobenzoic acid is based on the reaction of a diazonium salt solution (which was previously prepared from 2-aminobenzoic acid and nitrous acid [in turn prepared in situ from sodium nitrite and a strong acid, e.g. hydrochloric acid ] freshly at <5 ° C) with Hydrochloric acid and copper (I) chloride possible as a catalyst ( Sandmeyer reaction ).
properties
The chlorobenzoic acids are colorless to beige crystalline solids. The melting points differ significantly. The 4-chlorobenzoic acid, which has the highest symmetry, has the highest melting point. The chlorobenzoic acids have a higher acidity compared to benzoic acid due to the −I effect of the chlorine substituent. The pK s values are therefore correspondingly lower (benzoic acid: 4.20).
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d Entry on 2-chlorobenzoic acid in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on December 30, 2012(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ a b c d Entry on 3-chlorobenzoic acid in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on December 30, 2012(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ a b c d Entry on 4-chlorobenzoic acid in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on November 22, 2017(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ a b CRC Handbook of Tables for Organic Compound Identification , Third Edition, 1984, ISBN 0-8493-0303-6 .
- ^ Association of authors: Organikum , 19th edition, Johann Ambrosius Barth, Leipzig · Berlin · Heidelberg 1993, ISBN 3-335-00343-8 , pp. 367-368.
