Cinnamyl chloride
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
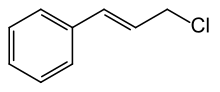
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Cinnamyl chloride | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 9 H 9 Cl | ||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 152.62 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
liquid |
||||||||||||||||||
| density |
1.10 g cm −3 |
||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
−19 ° C |
||||||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
108 ° C (16 h Pa ) |
||||||||||||||||||
| Refractive index |
1.584 (20 ° C) |
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . Refractive index: Na-D line , 20 ° C | |||||||||||||||||||
Cinnamyl chloride ( trans -3-phenylallyl chloride ) is one of the aromatics with a trans -substituted carbon-carbon double bond in the side chain. It is an allyl chloride substituted with a phenyl group . It is not to be confused with Cinnam o ylchlorid , the cinnamic acid chloride . The isomeric cis- cinnamyl chloride is of little importance. The information in this article relates only to trans -cinnamyl chloride.
Extraction and presentation
Cinnamyl chloride can be obtained by reacting cinnamyl alcohol and thionyl chloride or hydrochloric acid .
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f data sheet Cinnamyl chloride from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on March 23, 2011 ( PDF ).
- ^ Hermann Emde, Max Franke: Styrylaminverbindungen , in: Archiv der Pharmazie , 1909 , Volume 247, No. 3-9, pp. 333-350; doi : 10.1002 / ardp.19092470316 .


