Clevudin
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Non-proprietary name | Clevudin | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 10 H 13 FN 2 O 5 | |||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| Drug information | ||||||||||||||||
| ATC code | ||||||||||||||||
| Drug class | ||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 260.22 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
184-185 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
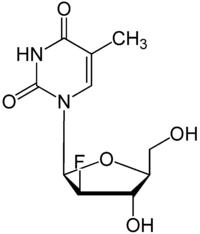
Clevudin , L-FMAU [short for 1- (2- F luoro-5- m ethyl-β, L- a rabinofuranosyl) u racil] is a chemical analogue of the nucleoside thymidine or its mirror-image enantiomer telbivudine , since it, like this one, has the reverse stereo configuration of thymidine. It is an antiviral selected from the group of nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors ( NRTI ) and is intended as a drug for the treatment of hepatitis B can be used.
Tried introduction as a drug
The drug was approved by the authorities there in 2006 as Levovir ® in South Korea for use against hepatitis B by the manufacturer Bukwang.
However, since late 2009, myopathy (muscle weakness) has been reported in patients treated with Clevudin for 6–8 months. The Phase III QUASH studies for the treatment of hepatitis B in the USA were subsequently discontinued by Pharmasset Inc. The majority of cases are said to have occurred after one year of treatment. The side effect is said to occur because clevudin is incorporated not only into viral, but also into mitochondrial DNA .
pharmacology
The nucleoside clevudine is phosphorylated to the nucleotide in the cell . In competition with the natural nucleotide deoxythymidine triphosphate (dTTP), clevudine triphosphate is incorporated into the DNA of viruses. The incorporation of the fluorine nucleoside triphosphate leads to chain termination and inhibition of the viral reverse transcriptase .
literature
- Analytics:
- WA Tao, L. Wu, RG Cooks, F. Wang, JA Begley, B. Lampert: Rapid enantiomeric quantification of an antiviral nucleoside agent (D, L-FMAU, 2'-fluoro-5-methyl-beta, D, L -arabinofurano-syluracil) by mass spectrometry . In: J. Med. Chem. Volume 44 , no. 22 , October 2001, p. 3541-3544 , PMID 11606118 .
- AS Xu, CK Chu, RE London: 19F NMR study of the uptake of 2'-fluoro-5-methyl-beta-L-arabinofuranosyluracil in erythrocytes: evidence of transport by facilitated and nonfacilitated pathways . In: Biochem. Pharmacol. tape 55 , no. 10 , May 1998, pp. 1611-1619 , PMID 9633997 .
- Synthesis:
- J. Du, Y. Choi, K. Lee, BK Chun, JH Hong, CK Chu: A practical synthesis of L-FMAU from L-arabinose . In: Nucleosides Nucleotides . tape 18 , no. 2 , February 1999, p. 187-195 , PMID 10067271 .
- T. Ma, JS Lin, MG Newton, YC Cheng, CK Chu: Synthesis and anti-hepatitis B virus activity of 9- (2-deoxy-2-fluoro-beta-L-arabinofuranosyl) purine nucleosides . In: J. Med. Chem. Volume 40 , no. 17 , August 1997, p. 2750-2754 , doi : 10.1021 / jm970233 + , PMID 9276020 .
- Pharmacology:
- I. Kocic: Clevudine University of Georgia / Abbott / Bukwang / Triangle / Yale University . In: Curr Opin Investig Drugs . tape 1 , no. 3 , November 2000, pp. 308-313 , PMID 11249713 .
- Triangle Pharmaceuticals, Inc.- Hepatitis B.
- SF Peek, PJ Cote, JR Jacob, IA Toshkov, WE Hornbuckle, BH Baldwin, FV Wells, CK Chu, JL Gerin, BC Tennant, BE Korba: Antiviral activity of clevudine [L-FMAU, (1- (2-fluoro- 5-methyl-beta, L-arabinofuranosyl) uracil)] against woodchuck hepatitis virus replication and gene expression in chronically infected woodchucks (Marmota monax) . In: Hepatology . tape 33 , no. 1 , January 2001, p. 254-266 , doi : 10.1053 / jhep.2001.20899 , PMID 11124844 .
- Use:
- H. clinker; New clinical pictures - hepatitis B and C co-infection (September 24, 2002).
Individual evidence
- ^ The Merck Index. An Encyclopaedia of Chemicals, Drugs and Biologicals , 14th Edition, 2006, ISBN 978-0-911910-00-1 , pp. 394-395.
- ↑ This substance has either not yet been classified with regard to its hazardousness or a reliable and citable source has not yet been found.
- ↑ Bukwang Launches New Hepatitis Drug . pharmaceuticalsinsight.com. November 2006. Archived from the original on October 16, 2013. Retrieved July 5, 2012.
- ↑ a b c R. D. Fleischer, AS Lok: Myopathy and neuropathy associated with nucleos (t) ide analog therapy for hepatitis B . In: J. Hepatol. tape 51 , no. 4 , October 2009, p. 787-791 , doi : 10.1016 / j.jhep.2009.06.011 , PMID 19665816 .
- ↑ BK Kim, J. Oh, SY Kwon, WH Choe, SY Ko, KH Rhee, TH Seo, SD Lim, CH Lee: Clevudine myopathy in patients with chronic hepatitis B . In: J. Hepatol. tape 51 , no. 4 , October 2009, p. 829-834 , doi : 10.1016 / j.jhep.2009.04.019 , PMID 19615776 .
- ↑ JI Seok, DK Lee, CH Lee, MS Park, SY Kim, HS Kim, HY Jo, CH Lee, DS Kim: Long-term therapy with clevudine for chronic hepatitis B can be associated with myopathy characterized by depletion of mitochondrial DNA . In: Hepatology . tape 49 , no. 6 , June 2009, p. 2080-2086 , doi : 10.1002 / hep.22959 , PMID 19333909 .