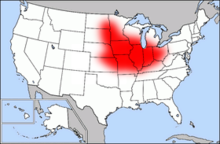
Corn Belt
Corn Belt is a name for a region in the Midwest of the USA , in which mainly corn (in American English : corn ) was traditionally grown. Primarily, this corn belt includes the territory of the states of Iowa , Indiana , Illinois, and Ohio , which are responsible for approximately 50 percent of the total corn cultivation in the United States. In addition, parts of the states of South Dakota , Nebraska , Kansas , Minnesota , Wisconsin , Michigan , Missouri and Kentucky are part of the Corn Belt .
In the meantime, the Corn Belt has become a corn, soy , pork , beef fattening belt . New varieties of hybrid maize enable cultivation to be expanded northwards, while on the other hand the state is restricting maize cultivation. The soybean, with its high yields per hectare and its high protein content, is an ideal fodder, partly takes the place of maize. In addition to traditional pig fattening, there is also cattle fattening, and dairy farming in the north. Recently, however, cattle fattening has declined due to competition from large farms in the Great Plains and California .
The term Grain Belt has also become established for the wheat and soy growing area, which partially overlaps with the Corn Belt .
In the North American Belt System , the Corn Belt is located between the Dairy Belt in the north and the Cotton Belt in the south.
literature
- JL Anderson: Industrializing the Corn Belt: Agriculture, Technology, and Environment, 1945-1972. Northern Illinois University Press, DeKalb 2016, ISBN 978-0-87580-741-6 .
- John C. Hudson: Making the Corn Belt: A Geographical History of Middle-Western Agriculture. Indiana University Press, Bloomington 1994, ISBN 978-0-253-32832-8 .
Web links
- Information from Britannica
- Information from infoplease