Dinoterb
| Structural formula | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
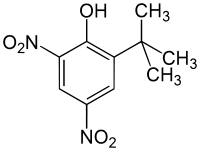
|
||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||
| Surname | Dinoterb | |||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 10 H 12 N 2 O 5 | |||||||||
| Brief description |
yellowish solid with a phenolic odor |
|||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||
|
||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||
| Molar mass | 240.22 g mol −1 | |||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||
| Melting point |
125.5–126.5 ° C (decomposition) |
|||||||||
| solubility |
very heavy in water (0.45 mg l −1 at pH 5 at 20 ° C) |
|||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||
|
||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||
Dinoterb is a chemical compound from the group of dinitrophenols .
properties
Dinoterb is a flammable solid that is poorly soluble in water. It decomposes when heated before it reaches its boiling point.
use
Dinoterb was used as a herbicide and a rodenticide . It was developed and introduced in 1963 by Pepro (later part of the Rhône-Poulenc company ).
Admission
The use of Dinoterb was banned based on an EU decision in 1997. In the EU states such as Germany and Austria as well as in Switzerland, no pesticides with this active ingredient are approved.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g Entry on Dinoterb in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on February 1, 2016(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ Entry on Dinoterp in the Pesticide Properties DataBase (PPDB) of the University of Hertfordshire , accessed on August 1, 2013.
- ↑ Entry on Dinoterb in the Classification and Labeling Inventory of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), accessed on February 1, 2016. Manufacturers or distributors can expand the harmonized classification and labeling .
- ↑ noaa: Dinoterp
- ↑ György Matolcsy, Miklós Nádasy, Viktor Andriska, Sándor Terényi: Pesticide chemistry, Volume 3 . Elsevier Science, 1989, ISBN 978-0-444-98903-1 ( page 580 in the google book search).
- ↑ European Commission - Directorate General for Agriculture: Review report for the active substance dinoterb. (PDF; 14 kB).
- ↑ General Directorate Health and Food Safety of the European Commission: Entry on Dinoterb in the EU pesticide database; Entry in the national registers of plant protection products in Switzerland , Austria and Germany ; Retrieved March 3, 2016.


