Nitrous oxide
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
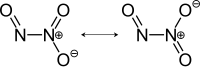
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Nitrous oxide | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
Nitrous anhydride, obsolete: nitrogen trioxide |
||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | N 2 O 3 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
deep dark blue liquid at −21 ° C |
||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 76.01 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
unstable under standard conditions |
||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
−100.7 ° C |
||||||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
−40– +3 ° C (partial decomposition) |
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||||||||
Dinitrogen trioxide is a chemical compound with the formula N 2 O 3 from the group of nitrogen oxides . It is the formal anhydride of nitrous acid . Below 3 ° C it is a deep blue liquid, which solidifies to a pale blue solid at −100.7 ° C.
properties
Dinitrogen trioxide is unstable at standard pressure above −40 ° C, as it dissociates into nitrogen monoxide NO and nitrogen dioxide NO 2 (or its dimer N 2 O 4 ) when it boils. This increases the boiling point of the mixture up to +3 ° C.
- Δ f H 0 gas : 91.2 kJ mol −1
- S 0 gas, 1 bar : 314.63 J (mol K) −1
Manufacturing
Dinitrogen trioxide is produced by contacting equal amounts of nitrogen monoxide (NO) and nitrogen dioxide (NO 2 ), whereby the mixture is cooled below −21 ° C. The two gases react with each other and combine to form the deep blue liquid nitrous oxide with the formula N 2 O 3 .
A convenient method of preparation is powdered arsenic trioxide with nitric acid to enable:
It is also formed as a gas at 20 ° C if solid sodium nitrite in conc. Reacts nitric acid.
use
Dinitrogen trioxide is the anhydride of the nitrous acid HNO 2 . This also occurs when nitrous oxide is introduced into water (H 2 O). However, if it is not further processed in a timely manner, it breaks down into nitrogen monoxide NO and nitric acid HNO 3 . Nitrites , the salts of nitrous acid , are sometimes made by adding nitrous oxide to the respective bases.
safety instructions
The decomposition products of nitrous oxide are toxic when inhaled. Serious damage is the result of contact with the eye.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c Entry on nitrogen oxides. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on April 17, 2014.
- ^ A b A. F. Holleman , E. Wiberg , N. Wiberg : Textbook of Inorganic Chemistry . 101st edition. Walter de Gruyter, Berlin 1995, ISBN 3-11-012641-9 , p. 696.
- ↑ There is not yet a harmonized classification for this substance . A labeling of Dinitrogen trioxide in the Classification and Labeling Inventory of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), retrieved on January 13, 2020, is reproduced from a self-classification by the distributor .
- ↑ G. Brauer (Ed.): Handbook of Preparative Inorganic Chemistry. 2nd Edition. Volume 1, Academic Press 1963, pp. 487-488.
- ↑ R. Stoermer and B. Kahlert: About the 1- and 2-bromo-coumarone . In: Reports of the German Chemical Society . 35 , 1633-1640 (1902), doi : 10.1002 / cber.19020350286 , page 1638




