Dopamine β-hydroxylase
| Dopamine β-hydroxylase | ||
|---|---|---|
| Properties of human protein | ||
| Mass / length primary structure | 578/617 amino acids | |
| Secondary to quaternary structure | Homotetramer | |
| Cofactor | PQQ , ascorbate , copper | |
| Identifier | ||
| Gene names | DBH ; DbetaH | |
| External IDs | ||
| Enzyme classification | ||
| EC, category | 1.14.17.1 , monooxygenase | |
| Response type | Hydroxylation | |
| Substrate | Dopamine + ascorbate + O 2 | |
| Products | Norepinephrine + dehydroascorbate + H 2 O | |
| Occurrence | ||
| Homology family | DBH | |
| Parent taxon | Higher mammals | |
When dopamine-β-hydroxylase (DBH) is the enzyme which the, oxidation of dopamine to noradrenaline catalyzed . This is the final step in the biosynthesis of the hormone and neurotransmitter norepinephrine. DBH has only been found in mammals , where it is primarily localized in the adrenal glands and the nervous system. Mutations in the human DBH - gene can dopamine β-hydroxylase deficiency lead.
Mice without DBH show no addictive behavior with certain drugs , but have unchanged appetite .
Catalyzed reaction
 + Ascorbate + O 2 →
+ Ascorbate + O 2 → 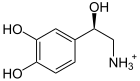 + dehydroascorbate + H 2 O
+ dehydroascorbate + H 2 O
Dopamine is hydroxylated to norepinephrine. DBH occurs in a cytosolic and a membrane isoform . The activity of the enzyme increases with age.
Individual evidence
- ↑ UniProt P09172
- ↑ Jasmin L, Narasaiah M, Tien D: Noradrenaline is necessary for the hedonic properties of addictive drugs . In: Vascul. Pharmacol. . 45, No. 4, October 2006, pp. 243-50. doi : 10.1016 / j.vph.2005.08.030 . PMID 16899413 .
- ↑ Erdös B, Erdem SR, Erdem A, Broxson CS, Tümer N: Effect of age on angiotensin II-mediated downregulation of adrenomedullary catecholamine biosynthetic enzymes . In: Exp. Gerontol. . 43, No. 8, August 2008, pp. 806-9. doi : 10.1016 / j.exger.2008.04.012 . PMID 18522866 .
Web links
Wikibooks: Biochemistry and Pathobiochemistry: Tyrosine Metabolism - Learning and Teaching Materials
- Jassal / D'Eustachio / reactome.org: Dopamine is oxidized to noradrenaline