Gellan
| Structural formula | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
High acyl gellan Gellan with low acyl content |
|||||||
| General | |||||||
| Surname | Gellan | ||||||
| other names | |||||||
| CAS number | 71010-52-1 | ||||||
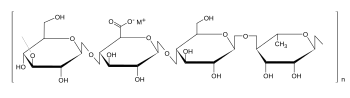
| Monomers / partial structures | Tetrasaccharide made up of a rhamnose , a glucuronic acid and two glucose units | ||||||
| Type of polymer | |||||||
| Brief description |
white-gray powder |
||||||
| properties | |||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||
| solubility |
|
||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||
|
|||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||
Gellan is a multiple sugar that is produced on a plant basis by means of microorganisms on a sugar-containing nutrient medium and is used in the food industry.
construction
Gellan belongs to the group of carbohydrates and, in a narrower sense, to the polysaccharides . Gellan has a linear structure, but in contrast to more well-known linear polysaccharides such as cellulose or amylose , which only consist of a single identical building block, consists of several different building blocks.
It consists of a rhamnose , a glucuronic acid and two glucose basic units, which are esterified with acetic acid and glyceric acid . Glucuronic acid is available as a mixed potassium , calcium , sodium and magnesium salt . The molar mass is approximately 500,000 g / mol .
Manufacturing
Gellan is made by the fermentation of carbohydrates by the bacterial strain Pseudomonas elodea . The culture broth is deacylated by heating (splitting off of the ester groups) and the gellan is precipitated therefrom with isopropyl alcohol , then dried and ground. Small amounts of nitrogenous residues usually remain in the product from the fermentation processes .
use
As a food additive ( E 418 ) it is used in the food industry as a gelling agent , thickening agent and stabilizer . It is mostly used for jams , fruit spreads, jams , confectionery , soy milk , etc. As dietary fiber , it is not absorbed by the body, it promotes digestion and has a laxative effect.
Gellan is also used in pharmaceutical preparations as a cation concentration-dependent gel former : in the absence of monovalent or divalent cations, it is in the sol state (colloidally dispersed) and swells to form a gel if these are present (e.g. in the tear fluid). This is used, for example, in eye drops to extend the time the drug remains on the eye and thus the time available for penetration. This can improve the local bioavailability and reduce the frequency of use.
As a gelling agent for nutrient media and plant cultures , it is used in microbiology as an alternative to agar and sold under trade names such as Nanogel-TC, Grovgel, AppliedGel, Phytagel or Gelrite. Since it can withstand temperatures of 120 ° C, it is of interest for the in vitro cultivation of thermophilic organisms.
Individual evidence
- ↑ Entry on E 418: Gellan gum in the European database for food additives, accessed on August 6, 2020.
- ↑ Entry on GELLAN GUM in the CosIng database of the EU Commission, accessed on August 6, 2020.
- ↑ a b c d e f g Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations - Corporate Document Repository - Gellan gum.
- ↑ Data sheet Phytagel ™ , BioReagent, plant cell culture tested, powder from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on January 2, 2013 ( PDF ).
- ↑ Entry on Gellan. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on June 15, 2014.
- ↑ ZZulV : Annex 4 (to Section 5, Paragraph 1 and Section 7) - Limited additives .
- ↑ Gelrite®: A novel, ion-activated, in-situ gelling polymer for ophthalmic vehicles. Effect on bioavailability of timolol. doi: 10.1016 / 0378-5173 (89) 90305-0 .
- ^ Pharmaceutical newspaper: Galenic tricks for use on the eye. Retrieved October 31, 2012.