Ash Moser Salt
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
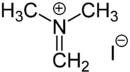
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Ash Moser Salt | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
N , N -dimethylmethaniminium iodide ( IUPAC ) |
||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 3 H 8 IN | ||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
light yellow solid |
||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 185.01 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
240 ° C ( decomposition ) |
||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
Decomposes in water |
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||||||||
The Eschenmoser salt is an organic salt . It consists of an N , N -dimethylmethylidene cation, usually with an iodide ion as a counterion. Other counter ions such as chloride or nitrate ions are also frequently used. The salt is named after its developer, the Swiss chemist Albert Eschenmoser .
The Eschenmoser salt is used for dimethylaminomethylation, so it can be used to introduce a dimethylaminomethyl function. For this purpose, the salt is reacted with a nucleophile . This attacks the carbon atom of the double bond .
presentation
There are several ways to synthesize Eschenmoser salt. Many of these are based on the reaction of tetra- N- methyl methanediamine with iodine-containing electrophiles such as diiodomethane or trimethylsilyl iodide . A more recent approach is the hydroiodide of dimethylamine and formaldehyde from
See also
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c data sheet dimethylmethylene ammonium iodide from AlfaAesar, accessed on April 14, 2010 ( PDF )(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ a b Data sheet N, N-Dimethylmethyleneiminium iodide from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on October 12, 2016 ( PDF ).
- ↑ GR Clark, GL Shaw, PWJ Surman, MJ Taylor, D. Steele in: J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 1994, 90, 20, 3139-3144.
- ↑ TA Bryson, GH Bonitz, CJ Reichel, RE Dardis in: J. Org. Chem. 1980 45, 3, 524-525.
- ↑ Tehrani, K. Abbaspour; De Kimpe, N. Science of Synthesis Volume27 Product class 8: iminium salts Pages313-348 2004
