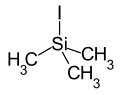
Iodotrimethylsilane
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Iodotrimethylsilane | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
Iodotrimethylsilyl iodide |
||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 3 H 9 ISi | ||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
Orange to brownish liquid with a pungent odor |
||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 200.09 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
liquid |
||||||||||||||||||
| density |
1.47 g cm −3 |
||||||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
107 ° C |
||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
Decomposes with water |
||||||||||||||||||
| Refractive index |
1.471 |
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . Refractive index: Na-D line , 20 ° C | |||||||||||||||||||
Iodotrimethylsilane is a chemical compound . It consists of a central silicon atom, which is surrounded in an almost tetrahedral manner by three methyl groups and one iodine substituent.
Manufacturing
Iodotrimethylsilane can be obtained in a Finkelstein- like reaction by reacting chlorotrimethylsilane with sodium iodide or magnesium iodide .
Another possibility is the cleavage of hexamethyldisilane or hexamethyldisiloxane by iodine .
properties
Iodotrimethylsilane is an orange to brownish liquid that boils at 107 ° C.
use
Iodotrimethylsilane can be used for the synthesis of Eschenmoser salt . To do this, it is reacted with tetra- N- methyl methanediamine.
Due to its Lewis acidic properties, it can also be used to open oxygen-containing heterocycles . An example of this is the opening of epoxies .
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e data sheet iodotrimethylsilane (PDF) from Merck , accessed on February 27, 2010.
- ↑ a b c data sheet iodotrimethylsilane from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on April 24, 2011 ( PDF ).
- ↑ C. Paolucci, L. Mattioli: Stereoisomeric Sugar-Derived Indolizines as Versatile Building Blocks: Synthesis of Enantiopure Di- and Tetrahydroxyindolizidines , in: J. Org. Chem. , 2001 , 66 , pp. 4787-4794; doi : 10.1021 / jo0016428 .
- ↑ U. Krüerke: Halogen exchange on chlorosilanes and the tetrahydrofuran cleavage by bromo- and iodosilanes , in: Chem. Ber. , 1962 , 95 , pp. 174-182; doi : 10.1002 / cber.19620950128 .
- ↑ EC Frederick, CB Abma, PF Vartanian: Metal-halogen bonding studies with group IV A trialkylmetal Halides , in: J. Organomet. Chem. , 1980 , 187 , pp. 203-211; doi : 10.1016 / S0022-328X (00) 81789-1 .
- ↑ ME Jung, MA Lyster: Quantitative dealkylation of alkyl ethers via treatment with trimethylsilyl iodide. A new method for ether hydrolysis , in: J. Org. Chem. , 1977 , 42 , pp. 3761-3764; doi : 10.1021 / jo00443a033 .
- ^ TA Bryson, GH Bonitz, CJ Reichel, RE Dardis: Performed Mannich salts: a facile preparation of dimethyl (methylene) ammonium iodide , in: J. Org. Chem. , 1980 , 45 , pp. 524-525; doi : 10.1021 / jo01291a032 .
- ↑ H. Poleschner, M. Heydenreich, D. Martin: Cyclic ethers as educts for the synthesis of butterfly pheromones , in: Synthesis , 1991 , 12 , pp. 1231-1235; doi : 10.1055 / s-1991-28425 .




