Sodium iodide
| Crystal structure | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
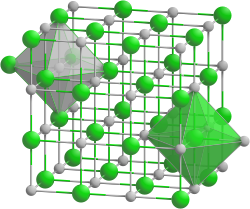
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| __ Na + __ I - | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Crystal system |
cubic |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Space group |
Fm 3 m (No. 225) |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Coordination numbers |
Na [6], I [6] |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Sodium iodide | |||||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
SODIUM IODIDE ( INCI ) |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Ratio formula | NaI | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless solid |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug information | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| ATC code | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 149.89 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| density |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
662 ° C |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
1304 ° C |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Refractive index |
1,774 |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . Refractive index: Na-D line , 20 ° C | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Sodium iodide (outdated sodium iodide) is a white, crystalline salt with the empirical formula Na I , which is used for the detection of ionizing radiation , for the treatment of iodine deficiency and for the production of iodine alkanes in the Finkelstein reaction .
Extraction and presentation
It can be obtained by reacting sodium carbonate with iron iodide . It is obtained as a dihydrate.
properties
The salt can be present as an anhydrous compound ( anhydrate ), di- or pentahydrate. Above 65 ° C the anhydrate crystallizes from aqueous solutions. Crystallization at room temperature gives the dihydrate. The pentahydrate can be obtained at lower temperatures between −13.5 ° C and −31.5 ° C.
| solvent | Solubility of NaI g NaI / 100 g solvent at 25 ° C |
|---|---|
| water | 184 |
| ammonia | 162 |
| Sulfur dioxide (liquid) | 15th |
| Methanol | 62.5-83.0 |
| Formic acid | 61.8 |
| Acetonitrile | 24.9 |
| acetone | 28.0 |
| Formamide | 57-85 |
| Dimethylformamide | 3.7-6.4 |
The standard enthalpy of formation of sodium iodide is ΔH f 0 = −288 kJ / mol.
use
Sodium iodide is widely used to treat and prevent iodine deficiency . The radioactive isotopes 123 iodine and 131 iodine are used as sodium iodide for nuclear medicine diagnostics - especially for thyroid scintigraphy . 131 Iodine is used in the form of sodium iodide in radioiodine therapy as a therapeutic agent.
Another area of application is the Finkelstein reaction . An alkyl chloride or bromide is treated with sodium iodide in acetone.
The better leaving group iodide displaces the worse leaving group chloride. The driving force behind the reaction is the low solubility of sodium chloride in acetone , which shifts the equilibrium to the side of the alkyl iodide. In addition to acetone, THF and acetonitrile can also be used as solvents.
There are also numerous reactions analogous to the Finkelstein reaction, such as B. the representation of trimethylsilyl iodide from trimethylsilyl chloride , acetyl iodide from acetyl chloride and much more
In crystals that are doped with thallium on part of the sodium positions (NaI: Tl + ), photons are generated by ionizing radiation and can thus be used as scintillation detectors , traditionally in nuclear medicine , geophysics , nuclear physics , etc. NaI: Tl + is the most widely used scintillation material as it produces the most light. The crystals are usually coupled with a photomultiplier and hermetically sealed because NaI is hygroscopic . Some parameters ( radiation hardness, afterglow, transparency) can be influenced by controlling the conditions under which the crystal grows. Crystals with higher doping are used as X-ray detectors with high spectroscopic quality. Sodium iodide can be used as a single crystal or polycrystalline .
Individual evidence
- ↑ entry to SODIUM IODIDE in the CosIng database of the European Commission, accessed on 17 April 2020th
- ↑ a b c d e f g Entry on sodium iodide in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on February 1, 2016(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ a b c Brockhaus ABC Chemie, FA Brockhausverlag Leipzig 1971, p. 924.
- ↑ Dimethyl Sulfoxide (DMSO) Solubility Data. Gaylord Chemical Company, LLC; Bulletin 102, June 2014, p. 14. (PDF)
- ↑ David R. Lide (Ed.): CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics . 90th edition. (Internet version: 2010), CRC Press / Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton, FL, Index of Refraction of Inorganic Crystals, pp. 10-247.
- ↑ Entry on sodium iodide in the ChemIDplus database of the United States National Library of Medicine (NLM) .
- ^ Burgess, J. Metal Ions in Solution (Ellis Horwood, New York, 1978) ISBN 0-85312-027-7 .
- ^ AF Holleman , E. Wiberg , N. Wiberg : Textbook of Inorganic Chemistry . 101st edition. Walter de Gruyter, Berlin 1995, ISBN 3-11-012641-9 , p. 1170.


