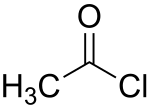
Acetyl chloride
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Acetyl chloride | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 2 H 3 ClO | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless liquid with a pungent odor |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 78.50 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
liquid |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
1.10 g cm −3 (20 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
−112 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
51 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| Vapor pressure |
309 h Pa (20 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
reacts violently with water |
|||||||||||||||
| Dipole moment | ||||||||||||||||
| Refractive index |
1.3886 (20 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| Thermodynamic properties | ||||||||||||||||
| ΔH f 0 |
−272.9 kJ / mol |
|||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . Refractive index: Na-D line , 20 ° C | ||||||||||||||||
Acetyl chloride or acetic acid chloride is a chemical, more precisely the functional chlorine derivative of acetic acid , in which the hydroxyl group of the acid is substituted by chlorine .
Extraction and presentation
Acetyl chloride is made by reacting calcium chloride with acetic anhydride . Alternatively, it can be obtained by reacting acetic acid with phosphorus (III) chloride . The synthesis from acetic acid and thionyl chloride or phosphorus (V) chloride is also possible, but gives poorer yields.
properties
Acetyl chloride is very volatile, it smokes in humid air as a result of the formation of HCl and has a strong irritant or corrosive effect on the respiratory tract. Like all carboxylic acid chlorides, acetyl chloride is very reactive. It reacts rapidly and exothermically with water to form acetic acid, with alcohols and phenols to form the corresponding esters, and with ammonia and primary and secondary amines , amides are formed. In each case, hydrogen chloride is split off.
use
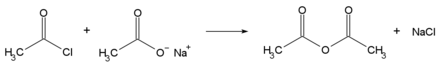
Acetyl chloride is mainly used for esterification and acetylation in chemical syntheses. But acetyl chloride is also used in the esterification of drugs ( acetylsalicylic acid ). Together with sodium acetate , it can be used to prepare acetic anhydride :
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g h Entry on acetyl chloride in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on January 10, 2017(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ David R. Lide (Ed.): CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics . 90th edition. (Internet version: 2010), CRC Press / Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton, FL, Dipole Moments, pp. 9-52.
- ↑ David R. Lide (Ed.): CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics . 90th edition. (Internet version: 2010), CRC Press / Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton, FL, Physical Constants of Organic Compounds, pp. 3-6.
- ↑ Entry on Acetyl chloride in the Classification and Labeling Inventory of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), accessed on February 1, 2016. Manufacturers or distributors can expand the harmonized classification and labeling .
- ↑ David R. Lide (Ed.): CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics . 90th edition. (Internet version: 2010), CRC Press / Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton, FL, Standard Thermodynamic Properties of Chemical Substances, pp. 5-21.
- ^ Association of authors: Organikum , 19th edition, Johann Ambrosius Barth, Leipzig · Berlin · Heidelberg 1993, ISBN 3-335-00343-8 , pp. 439f.