Sodium fluoride
| Crystal structure | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
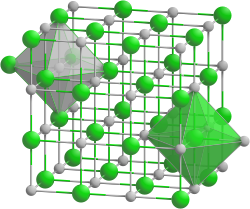
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| __ Na + __ F - | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Crystal system |
cubic |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Space group |
Fm 3 m (No. 225) |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Coordination numbers |
Na [6], F [6] |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Sodium fluoride | |||||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Ratio formula | NaF | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless and odorless solid |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug information | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| ATC code | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 41.99 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| density |
2.78 g cm −3 |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
993 ° C |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
1704 ° C |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Refractive index |
1.3252 |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| MAK |
1 mg m −3 |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Thermodynamic properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| ΔH f 0 |
−575 kJ / mol |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . Refractive index: Na-D line , 20 ° C | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Sodium fluoride is a sodium salt of hydrofluoric acid ( hydrofluoric acid ).
Occurrence
Sodium fluoride occurs naturally only in the form of the rare mineral villiaumite .
Extraction and presentation
Neutralization of concentrated hydrofluoric acid with sodium hydroxide solution
Excess hydrogen fluoride leads to the formation of sodium hydrogen fluoride :
Conversion of hydrofluoric acid with sodium carbonate :
Starting from the sodium salt of hexafluorosilicic acid , sodium fluoride can be obtained by thermal decomposition.
properties
The colorless sodium fluoride crystallizes in the sodium chloride structure and can be “grown” into single crystals . It is permeable to infrared and UV light. It is only sparingly soluble in water at all temperatures. Heating hardly increases the solubility. It does not dissolve in ethanol . In concentrated sulfuric acid , it is converted to sodium sulfate and hydrogen fluoride . As a result of partial hydrolysis , the aqueous solution of sodium fluoride has a slightly alkaline reaction . Sodium fluoride acts as an insecticide and is poisonous.
Sodium fluoride forms melts with one eutectic with sodium chloride , sodium carbonate and calcium fluoride , and melts with two eutectics with sodium sulfate. Liquid sodium fluoride conducts the electrical current, with the resistance decreasing with increasing temperature.
Responsiveness
Sodium fluoride and sulfuric acid react to form sodium sulfate and hydrogen fluoride.
The high toxicity of NaF compared to other sodium halides (e.g. sodium chloride) is due to the effect of the fluoride anion as a strong Lewis base . The fluoride binds to all iron-containing enzymes and thus blocks them.
The fluoride ions block the calcium and magnesium metabolism and inhibit important enzymes. This leads to acutely threatening metabolic disorders, which can be fatal with multiple organ failure.
use

Sodium fluoride is used as a wood preservative and to preserve adhesives. In the electrolytic extraction of aluminum it is used as a flux and in metallurgy as a slag additive for molten metal.
Other uses:
- Fluoridation of drinking water , table salt , toothpaste , etc., fluorine tablets
- As enzyme poison in the blood in so-called plasma lactate blood collection tubes for glucose and lactate in the blood
- Fluorinating agents in organic chemistry.
- Opacifiers and fluxes in glass production
- For cleaning other fluorides by binding excess hydrogen fluoride
- Single crystals are used in instrumental analysis as filters, lenses and prisms
- In photometry as a masking agent for iron ions
- Purification of uranium hexafluoride during reprocessing
- As a phosphatase inhibitor in molecular biology
- With the cyclotron product Fluor-18 as a radiopharmaceutical for skeletal scintigraphy using positron emission tomography (or in the 1970s using a rectilinear scanner and ultra-high-energy collimator).
Precautions
Sodium fluoride is toxic. Avoid inhalation of dust. Gloves should be worn when working with sodium fluoride. An amount of 5–10 g for a person weighing 70 kg is generally regarded as lethal . However, deaths have already been observed from a dose of 15 mg / kg, which corresponds to an amount of sodium fluoride of 1.05 g in a person weighing 70 kg. For these reasons, an amount of 5 mg / kg is already regarded as a critical threshold, since serious, life-threatening symptoms of poisoning can already occur from this point, which require immediate emergency treatment .
Individual evidence
- ↑ Entry on SODIUM FLUORIDE in the CosIng database of the EU Commission, accessed on April 17, 2020.
- ↑ a b c d e f g Entry on sodium fluoride in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on February 1, 2016(JavaScript required) .
- ^ H. Kojima, SG Whiteway, CR Masson: Melting points of inorganic fluorides . In: Canadian Journal of Chemistry . 46 (18), 1968, pp. 2968-2971, doi : 10.1139 / v68-494 .
- ↑ Entry on sodium fluoride. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on December 25, 2014.
- ↑ David R. Lide (Ed.): CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics . 90th edition. (Internet version: 2010), CRC Press / Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton, FL, Index of Refraction of Inorganic Crystals, pp. 10-247.
- ↑ Entry on sodium fluoride in the Classification and Labeling Inventory of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), accessed on February 1, 2016. Manufacturers and / or distributors can expand the harmonized classification and labeling .
- ^ A b c B. Martel, K. Cassidy: Chemical Risk Analysis: A Practical Handbook. Butterworth – Heinemann, 2004, ISBN 1-903-99665-1 , p. 363.
- ^ AF Holleman , E. Wiberg , N. Wiberg : Textbook of Inorganic Chemistry . 101st edition. Walter de Gruyter, Berlin 1995, ISBN 3-11-012641-9 , p. 1170.
- ↑ G. Brauer (Ed.), Handbook of Preparative Inorganic Chemistry 2nd ed., Vol. 1, Academic Press 1963, pp. 235-236.
- ↑ a b c d Fluorine compounds in oral hygiene products (PDF; 332 kB)
- ↑ Additives of various blood collection tubes (English). ( Memento of the original from September 23, 2015 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.






