Rubidium fluoride
| Crystal structure | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| __ Rb + __ F - | |||||||||||||||||||
| Crystal system |
cubic |
||||||||||||||||||
| Space group |
Fm 3 m (No. 225) |
||||||||||||||||||
| Lattice parameters |
a = 565 pm |
||||||||||||||||||
| Coordination numbers |
Rb [6], F [6] |
||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Rubidium fluoride | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
Rubidium (I) fluoride |
||||||||||||||||||
| Ratio formula | RbF | ||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
white odorless solid |
||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 104.46 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||||||||||||||
| density |
3.58 g cm −3 |
||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
795 ° C |
||||||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
1410 ° C |
||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
1306 g l −1 in water at 18 ° C |
||||||||||||||||||
| Refractive index |
1.397 |
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| MAK |
2.5 mg m −3 (as fluoride) |
||||||||||||||||||
| Thermodynamic properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| ΔH f 0 |
−552.2 kJ mol −1 |
||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . Refractive index: Na-D line , 20 ° C | |||||||||||||||||||
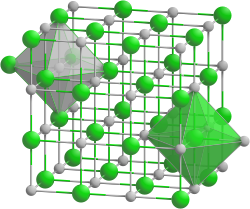
Rubidium fluoride is a chemical compound between rubidium and fluorine . It does not occur in nature and easily dissolves in water. It's a to fluorides scoring salt , which in the sodium chloride structure crystallized.
Extraction and presentation
Rubidium can by reaction of hydrogen fluoride with rubidium or rubidium hydroxide , and subsequent drying receive:
properties
It is a white crystalline substance with a cubic crystal structure , which looks very similar to table salt (NaCl). The crystals belong to the space group Fm 3 m (space group no. 225) with the lattice parameter a = 565 pm and four formula units per unit cell . The refractive index of the crystals is n D = 1.398. Rubidium fluoride colors a flame ( Bunsen burner flame ) purple or magenta (spectral analysis).
Rubidium fluoride forms two different hydrates, a sesquihydrate with the stoichiometric composition 2RbF · 3H 2 O and a third hydrate with the composition 3RbF · H 2 O.
In addition to the simple rubidium fluoride, an acidic rubidium fluoride with the empirical formula HRbF 2 is known, which can be produced by the reaction of rubidium fluoride and hydrogen fluoride. The compounds H 2 RbF 3 and H 3 RbF 4 were also synthesized.
The solubility in acetone is 0.0036 g / kg at 18 ° C and 0.0039 g / kg at 37 ° C.
The standard enthalpy of formation of rubidium fluoride is Δ f H 0 298 = −552.2 kJ mol −1 , the standard free enthalpy of formation ΔG 0 298 = −520.4 kJ mol −1 , and the standard molar entropy S 0 298 = 113.9 J. K −1 mol −1 . The enthalpy of solution of rubidium fluoride was determined to be −24.28 kJ / mol.
safety instructions
Due to the fluoride it contains, contact with the skin and swallowing should be avoided when handling rubidium fluoride .
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f data sheet rubidium fluoride at AlfaAesar, accessed on January 29, 2010 ( PDF )(JavaScript required) . .
- ↑ David R. Lide (Ed.): CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics . 90th edition. (Internet version: 2010), CRC Press / Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton, FL, Index of Refraction of Inorganic Crystals, pp. 10-247.
- ↑ a b Data sheet Rubidium fluoride from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on April 22, 2011 ( PDF ).
- ↑ a b c d R. E. Dickerson, HB Gray, H.-W. Sighting, MY Darensbourg: Principles of Chemistry . Walter de Gruyter, 1988, ISBN 978-3-11-009969-0 , p. 976 ( limited preview in Google Book Search [accessed December 1, 2018]).
- ↑ a b c H. Eggeling, J. Meyer: About the fluorides of rubidium . In: Journal of Inorganic Chemistry . tape 46 , 1905, pp. 174 ff . ( Full text ).
- ^ A b Jean D'Ans, Ellen Lax: Paperback for chemists and physicists . 3. Elements, inorganic compounds and materials, minerals. 4th edition. tape 3 . Springer, 1997, ISBN 978-3-540-60035-0 , pp. 686 ( limited preview in Google Book Search [accessed December 1, 2018]).
- ↑ M. de Forcrand: Sur les hydrates des fluorures de rubidium et de cesium . In: Compt. Rend. Hebd. tape 152 , 1911, pp. 1208 ( full text ).
- ↑ Han Eggerling, Julius Meyer: About the fluorides of rubidium . In: Journal of Inorganic Chemistry . tape 46 , no. 1 , 1905, pp. 174-176 , doi : 10.1002 / zaac.19050460111 .
- ^ A Text-Book of Inorganic Chemistry . Forgotten Books, ISBN 978-1-4510-0469-4 , pp. 209 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ Aterton Seidell: Solubilities Of Organic Compounds . tape 1 , p. 1437 ( full text ).
- ↑ M. de Forcrand: Étude thermochimique de quelques composés binaires des métaux alcalins et alcalino-terreux . In: Compt. Rend. Hebd. tape 152 , 1911, pp. 27 f . ( Full text ).



