Cesium fluoride
| Crystal structure | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
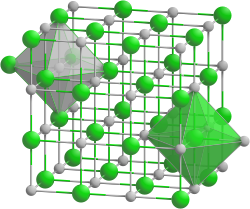
|
||||||||||||||||
| __ Cs + __ F - | ||||||||||||||||
| Crystal system |
cubic |
|||||||||||||||
| Space group |
Fm 3 m (No. 225) |
|||||||||||||||
| Coordination numbers |
Cs [6], F [6] |
|||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Cesium fluoride | |||||||||||||||
| Ratio formula | CsF | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless, crystalline solid |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 151.90 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
4.12 g cm −3 |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
682 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
1251 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
soluble in water (3670 g l −1 at 18 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| Refractive index |
1.477 |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| MAK |
2.5 mg m −3 (as fluoride) |
|||||||||||||||
| Thermodynamic properties | ||||||||||||||||
| ΔH f 0 |
−555 kJ / mol |
|||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . Refractive index: Na-D line , 20 ° C | ||||||||||||||||
Cesium fluoride ( CsF ) is the cesium salt of hydrofluoric acid . It is a colorless, hygroscopic , crystalline solid that dissolves well in polar solvents. In addition to tetraalkylammonium fluorides (such as tetrabutylammonium fluoride TBAF), it is used in chemistry as a supplier of “naked” fluoride ions and mild bases . In addition, it has a strongly pronounced ionic character and, in addition to the unstable and rare francium fluoride, is the combination of the two elements with the greatest possible difference in electronegativities .
presentation
Cesium fluoride can be obtained by reacting hydrogen fluoride with cesium carbonate or cesium hydroxide and then drying.
properties

Because of its good solubility and easy availability, cesium fluoride can be used as a fluoride ion donor . It is more soluble than its relatives with the smaller alkali metals sodium and potassium .
Because of the only slightly pronounced nucleophilicity of the fluoride ions, cesium fluoride is used as a mild base in organic chemistry , e.g. B. in the Knoevenagel reaction . It is also used for desilylation, i.e. H. for the removal of silyl - protective groups , since due to the high bond energy of Si-F bond is a strong tendency to form consists Selbiger. In addition, cesium fluoride can be dehydrated without any problems, so that it can also be used on acid and water-sensitive substrates.
safety instructions
The reaction with acids leads to the formation of toxic hydrogen fluoride .
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f data sheet cesium fluoride at AlfaAesar, accessed on February 3, 2010 ( PDF )(JavaScript required) . .
- ↑ David R. Lide (Ed.): CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics . 90th edition. (Internet version: 2010), CRC Press / Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton, FL, Index of Refraction of Inorganic Crystals, pp. 10-246.
- ↑ a b data sheet cesium fluoride from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on March 15, 2011 ( PDF ).
- ^ AF Holleman , E. Wiberg , N. Wiberg : Textbook of Inorganic Chemistry . 101st edition. Walter de Gruyter, Berlin 1995, ISBN 3-11-012641-9 , p. 1170.
literature
- GK Friestad, BP Branchaud, in: Handbook of Reagents for Organic Synthesis: Acidic and Basic Reagents , (HJ Reich, JH Rigby, eds.), Pp. 99-103, Wiley, New York, 1999.
- L. Rand, JV Swisher, CJ Cronin, Journal of Organic Chemistry , 27 , p. 3505 (1962).
- M. Fiorenza, A. Mordini, S. Papaleo, S. Pastorelli, A. Ricci, Tetrahedron Letters , 26 , p. 787 (1985).
- Evans FW, Litt MH, Weidler-Kubanek AM, Avonda FP, Journal of Organic Chemistry , 33 , pp. 1837-1839 (1968).



