Potassium fluoride
| Crystal structure | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||||||||||||
| __ K + __ F - | ||||||||||||||||
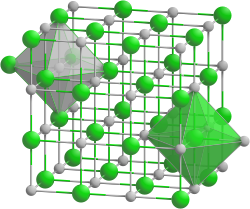
| Crystal system |
cubic |
|||||||||||||||
| Space group |
Fm 3 m (No. 225) |
|||||||||||||||
| Coordination numbers |
K [6], F [6] |
|||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Potassium fluoride | |||||||||||||||
| Ratio formula | Theatrical Version | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
white, hygroscopic powder |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 58.10 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
2.48 g cm −3 (20 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
852 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
1502 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
good in water (485 g l −1 at 20 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| Refractive index |
1.362 |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| MAK |
1 mg m −3 |
|||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . Refractive index: Na-D line , 20 ° C | ||||||||||||||||
Potassium fluoride is a chemical compound from the group of fluorides .
Occurrence
Potassium fluoride occurs naturally in the form of the rare mineral carobbiite .
properties
Potassium fluoride is a white, hygroscopic powder that normally occurs as a dihydrate. The dihydrate already melts at 46 ° C in its own crystal water . Aqueous potassium fluoride solutions react weakly as a result of hydrolysis . 485 g of potassium fluoride dissolve in one liter of water at 20 ° C.
The standard enthalpy of formation of potassium fluoride is Δ H f 0 = −569 kJ / mol.
Potassium contains 0.0118% of the isotope 40 K, this provides 20979 Bq per kilogram of KF, of which 89.28% is beta radiation and 10.72% is gamma radiation with 1.46083 MeV.
synthesis
Potassium fluoride can be made by neutralizing hydrofluoric acid with potassium carbonate or potassium hydroxide . Acid potassium hydrogen difluoride (KHF 2 ) crystallizes from solutions with excess hydrofluoric acid , which can be converted into potassium fluoride (KF) by heating.
use
Potassium fluoride is used in enamel production for the production of glazes, as a cement additive, as an oxide-dissolving component of aluminum welding powders , as a wood preservative and for glass etching. It can also be found in articles on oral hygiene (toothpaste, mouthwash, etc.) and as an eponymous additive in fluoridated table salt.
In organic chemistry, potassium fluoride is used to convert organochlorine compounds into fluorocarbons .
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g Entry on potassium fluoride in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on February 1, 2016(JavaScript required) .
- ^ H. Kojima, SG Whiteway, CR Masson: Melting points of inorganic fluorides . In: Canadian Journal of Chemistry . 46 (18), 1968, pp. 2968-2971, doi : 10.1139 / v68-494 .
- ↑ David R. Lide (Ed.): CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics . 90th edition. (Internet version: 2010), CRC Press / Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton, FL, Index of Refraction of Inorganic Crystals, pp. 10-246.
- ↑ Entry on Potassium fluoride in the Classification and Labeling Inventory of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), accessed on February 1, 2016. Manufacturers or distributors can expand the harmonized classification and labeling .
- ^ AF Holleman , E. Wiberg , N. Wiberg : Textbook of Inorganic Chemistry . 101st edition. Walter de Gruyter, Berlin 1995, ISBN 3-11-012641-9 , p. 1170.
- ↑ G. Brauer (Ed.), Handbook of Preparative Inorganic Chemistry 2nd ed., Vol. 1, Academic Press 1963, pp. 236-7.
- ^ AI Vogel, J. Leicester, WAT Macey: n-Hexyl Fluoride In: Organic Syntheses . 36, 1956, p. 40, doi : 10.15227 / orgsyn.036.0040 ; Coll. Vol. 4, 1963, p. 525 ( PDF ).

