Patchwork
| Patchwork | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

Fleckenmusang ( Paradoxurus hermaphroditus ) |
||||||||||||
| Systematics | ||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
| Scientific name | ||||||||||||
| Paradoxurus hermaphroditus | ||||||||||||
| ( Pallas , 1777) |
The spotted musang ( Paradoxurus hermaphroditus ) is a species of crawling cat from the genus of the musangs that is widespread in South and Southeast Asia . He is best known for his role in the production of Kopi Luwak coffee .
description
The rough, thick fur of the Fleckenmusang has a gray basic color. They have black vertical stripes on their backs and black, lengthwise spots on their shoulders and sides. The feet, ears and muzzle are also colored black, the face has a black and white, raccoon-like mask drawing. The specific epithet hermaphroditus in the scientific name of Fleckenmusang comes from the testicle-like scent glands that both sexes have below the tail. Fleckenmusangs reach a head body length of 48 to 59 centimeters, the monochrome black tail is 44 to 54 centimeters long. Their weight is around 2.5 to 4 kilograms.
distribution and habitat
The habitat of the Fleckenmusangs is predominantly tropical rainforest .
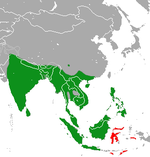
Fleckenmusangs are native to all of South and Southeast Asia, their distribution area includes India and Sri Lanka , southern China including the island of Hainan , Vietnam , Laos and Thailand . Musangs in Myanmar , Thailand, Cambodia , partly from Vietnam, Malaya , Sumatra , Java , Nias , Bangka , Flores , Bali and Roti , which used to be part of the patch musangs, are now regarded as a separate species of Paradoxurus musangus . Musangs in the Philippines , Borneo and the Mentawai Islands are now assigned to the species Paradoxurus philippinensis . Musangs came to the islands east of Java and Borneo in prehistoric times through humans and spread there. Which of the species the musangs on Sulawesi , Timor and other islands of the Malay Archipelago belong to has not yet been researched.
Way of life
Like most crawling cats, the spotted musang is a nocturnal animal. It is primarily a tree dweller and is good at climbing. During the day he slept in knotholes and hollow trunks. He lives solitary outside of the mating season.
In some places Fleckenmusangs have developed into cultural followers and now live in villages where they have moved into attics and stables. As a cause of nocturnal noise, they are just as unpopular in Southeast Asia as the stone marten is in Europe . Musangs are also said to cause damage when they enter coffee plantations .
As an omnivore, it looks for fruits as well as insects , worms and bird eggs at night . With luck it will also catch a bird or a squirrel .
After a gestation period of around 60 days, the female gives birth to two to five young animals in a tree cavity. These are weaned after around 11 to 12 months. The highest known age of an animal in captivity was over 25 years.
use
In southern China, the flecked musang is hunted for human consumption, partly as bushmeat . Indian tribes also hunt it for consumption.
In Southeast Asia, the famous Kopi Luwak coffee is produced with the help of the Fleckenmusang . The name comes from the Indonesian word "Kopi" for coffee, "Luwak" is the native name of this animal. Fleckenmusangs eat the coffee cherries and excrete them again with almost no accompanying products. In the digestive tract of this animal, the coffee beans are subjected to fermentation by enzymes , which changes the taste characteristics: allegedly, a dark and full, but also somewhat musty aroma is created.
The Fleckenmusang has not yet been listed as an endangered species. Nevertheless, wild animals for industrialized Luwak coffee production are bothering him. The animals are kept in barren lattice cages (similar to battery chicken rearing) and mostly fed with coffee berries, which leads to malnutrition, stressful behavior and a significant death rate.
literature
- Ronald M. Nowak: Walker's Mammals of the World . 6th edition. Johns Hopkins University Press, Baltimore 1999, ISBN 0-8018-5789-9 (English).
Individual evidence
- ↑ Géraldine Veron, Marie-Lilith Patou, Mária Tóth, Manori Goonatilake & Andrew P. Jennings: How Many Species of Paradoxurus Civets are there? New Insights from India and Sri Lanka. Journal of Zoological Systematics and Evolutionary Research, 1-14, 2014 doi : 10.1111 / jzs.12085
Web links
- Paradoxurus hermaphroditus in the endangered Red List species the IUCN 2006. Posted by: Mustelid Specialist Group, 1996. Retrieved on 12 May, 2006.
- Observations of small carnivores in Jakarta wildlife markets, Indonesia, with notes on trade in Javan Ferret Badger Melogale orientalis and on the increasing demand for Common Palm Civet Paradoxurus hermaphroditus for civet coffee production. Chris R. Sheffert. Small Carnivore Conservation, Vol. 47: 38-41, December 2012.