Fludarabine
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
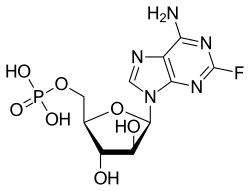
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Non-proprietary name | Fludarabine | |||||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
{[(2 R , 3 S , 4 S , 5 R ) -5- (6-amino-2-fluoro-9 H -purin-9-yl) -3,4-dihydroxyoxolan-2-yl] methoxy} phosphate ( IUPAC ) |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 10 H 13 FN 5 O 7 P | |||||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug information | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| ATC code | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 365.21 g · mol -1 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
soluble in DMSO |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Fludarabine is a cytostatic from the group of purine analogues .
properties
Fludarabine or fludarabine (Fludara-5-dihydrogen phosphate) is a fluorinated nucleotide - analogue of vidarabine and belongs to the group of purine analogs. It contains - in contrast to most of nucleotides - instead of β- D -Ribofuranose the β- D -Arabinofuranose . Furthermore, the adenine is substituted by fluorine in the 2-position.
Fludarabine is after intravenous administration in the body cells to the active metabolite fludarabine ATP phoshoryliert . In this form it is actually effective. It prevents DNA synthesis by inhibiting ribonucleotide reductase and DNA polymerase . In addition, the fludarabine nucleotide is incorporated into the DNA and thus leads to apoptosis of the cell. Fludarabine thus has cytotoxic properties.
use
Fludarabine is used to treat low-grade non-Hodgkin lymphoma , acute leukemia and chronic lymphocytic leukemia ( CLL ).
Side effects
The main side effects are often pronounced myelosuppression and immunosuppression , which lead to an increased susceptibility to infections. A common bone marrow suppression can cause anemia , thrombocytopenia, and neutropenia . CD4 + helper cells, CD8 + suppressor cells and natural killer cells (NK cells) as well as immunoglobulins are often reduced. In addition, as with other cytotoxic drugs, nausea, loss of appetite, weakness and fever can occur.
Web links
- Entry for Fludarabine in the Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) , accessed October 16, 2013.
Individual evidence
- ↑ Selleckchem: Fludarabine
- ↑ a b Data sheet 2-Fluoroadenine-9-β-D-arabinofuranoside from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on November 7, 2016 ( PDF ).
- ^ Valentino J. Stella: Prodrugs challenges and rewards. P. 1 . Springer Science & Business Media, 2007, ISBN 978-0-387-49782-2 , pp. 173 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ Michael Freissmuth, Stefan Offermanns, Stefan Böhm: Pharmacology and Toxicology From the Molecular Basics to Pharmacotherapy . Springer Science & Business Media, 2012, ISBN 978-3-642-12353-5 , pp. 742 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ Christian Buske: Indolent lymphoma pathophysiology, prognostic factors and current therapy recommendations; with 42 tables . Deutscher Ärzteverlag, 2011, ISBN 978-3-7691-0569-8 , p. 132 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ^ A b Thomas Kroner, Anita Margulies, Christian Taverna, Cristina Studer: Medicines in Tumor Therapy Manual for Nursing Practice . Springer-Verlag, 2013, ISBN 978-3-642-36940-7 , p. 108 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ Dietmar P. Berger, Rupert Engelhardt, Roland Mertelsmann: The Red Book Hematology and Internal Oncology . Hüthig Jehle Rehm, 2013, ISBN 978-3-609-51218-1 , pp. 709 ( limited preview in Google Book search).