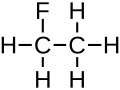
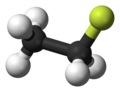
Fluoroethane
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
||||||||||||||||
| Representation in skeletal formula notation | ||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Fluoroethane | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 2 H 5 F | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
extremely flammable gas |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 48.06 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
gaseous |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
−143 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
−37.1 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| Vapor pressure |
|
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
slightly soluble in water |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| Global warming potential |
4 (based on 100 years) |
|||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Fluoroethane is a chemical compound from the group of saturated fluorocarbons .
Extraction and presentation
Fluoroethane can be obtained by reacting ethene with hydrogen fluoride or by reacting chloroethane with silver (I) fluoride .
properties
Fluoroethane is an extremely flammable gas that is sparingly soluble in water. It decomposes when heated, producing, among other things, hydrogen fluoride . Its critical temperature is 102.3 ° C., the critical pressure 50.3 bar and the critical density 0.8176 g / cm 3 .
Fluoroethane forms flammable vapor-air mixtures. The explosion range is between 5% by volume (100 g / m 3 ) as the lower explosion limit (LEL) and 10% by volume (200 g / m 3 ) as the upper explosion limit (UEL).
The fluoroethane molecule can be represented with different formulas:
use
Fluoroethane can be used as a refrigerant, but due to its properties has practically no industrial importance.
safety instructions
Fluoroethane forms an explosive mixture with air.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n Entry for CAS no. 353-36-6 in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on October 28, 2019(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ G. Myhre, D. Shindell et al .: Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis . Working Group I contribution to the IPCC Fifth Assessment Report. Ed .: Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change . 2013, Chapter 8: Anthropogenic and Natural Radiative Forcing, pp. 24-39; Table 8.SM.16 ( PDF ).
- ↑ Dr. PB Saxena: IIT Chemistry . S. O-218 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ Jiangtao Wu, Yong Zhou: An Equation of State for Fluoroethane (R161). In: International Journal of Thermophysics. 33, 2012, pp. 220-234, doi: 10.1007 / s10765-011-1151-3 .
- ↑ Peter Fabian, Onkar N. Singh: Reactive halogen compounds in the atmosphere . Springer, 1999, ISBN 3-540-64090-8 , pp. 87 ( limited preview in Google Book search).