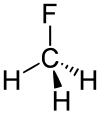
Fluoromethane
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Fluoromethane | |||||||||||||||
| other names | ||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | CH 3 F | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
extremely flammable colorless gas |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 34.03 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
gaseous |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
−137.8 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
−78.4 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| Vapor pressure |
3.3 M Pa at 20 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
good in water (2.3 g l −1 at 20 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| Dipole moment | ||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| Global warming potential |
141 (based on 100 years) |
|||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Fluoromethane is a highly flammable chemical compound from the group of fluorocarbons that is gaseous at room temperature .
properties
The fluoromethane molecule is strongly polar due to the high electronegativity of fluorine , which leads to a solubility of 2.3 g · l −1 water (at 20 ° C). Fluoromethane has a critical temperature of 44.55 ° C, the critical pressure is 58.742 bar and the critical density is 0.30 kg / l. The triple point temperature is −137.8 ° C, which corresponds to the melting temperature. Its specific heat capacity at 25 ° C is C p = 38.171 Jmol −1 K −1 . The compound has a global warming potential of 141.
use
Fluoromethane is used in the production of semiconductors as an etching gas and in plasma etching . It was also used as a refrigerant .
safety instructions
Fluoromethane forms an explosive mixture with air. Due to the lack of odor, pollution in the air is not perceptible. Toxic effects on organisms are not known. Burning can produce highly toxic hydrogen fluoride . As with other fluorocarbons and chlorofluorocarbons, a narcotic effect is suspected.
Web links
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g h i j k Entry on fluoromethane in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on February 9, 2017(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ a b c product data sheet fluoromethane at AirLiquide , accessed on February 9, 2017.
- ↑ David R. Lide (Ed.): CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics . 90th edition. (Internet version: 2010), CRC Press / Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton, FL, Permittivity (Dielectric Constant) of Gases, pp. 6-188.
- ↑ G. Myhre, D. Shindell et al .: Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis . Working Group I contribution to the IPCC Fifth Assessment Report. Ed .: Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change . 2013, Chapter 8: Anthropogenic and Natural Radiative Forcing, pp. 24-39; Table 8.SM.16 ( PDF ).
- ↑ Safety data sheet fluoromethane (PDF; 38 kB). Air Liquide, accessed July 15, 2017.

