Fumarase
| Fumarase | ||
|---|---|---|
|
||
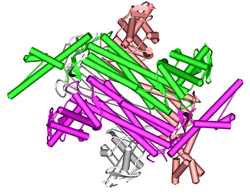
| Model of the tetramer of human fumarase according to PDB 3E04 | ||
| Properties of human protein | ||
| Mass / length primary structure | 466 amino acids | |
| Secondary to quaternary structure | Tetramer | |
| Isoforms | 2 | |
| Identifier | ||
| Gene name | FH | |
| External IDs |
|
|
| Enzyme classification | ||
| EC, category | 4.2.1.2 , lyase | |
| Response type | Hydration | |
| Substrate | L -Malat; Fumarate + H 2 O | |
| Products | Fumarate + H 2 O; L -Malat | |
| Occurrence | ||
| Homology family | Fumarase II | |
| Parent taxon | Creature | |
| Orthologue | ||
| human | House mouse | |
| Entrez | 2271 | 14194 |
| Ensemble | ENSG00000091483 | ENSMUSG00000026526 |
| UniProt | P07954 | P97807 |
| Refseq (mRNA) | NM_000143 | NM_010209 |
| Refseq (protein) | NP_000134 | NP_034339 |
| Gene locus | Chr 1: 241.5 - 241.52 Mb | Chr 1: 175.6 - 175.63 Mb |
| PubMed search | 2271 |
14194
|
Fumarase (more precisely: fumarate hydratase ) are enzymes that catalyze the addition of water to fumarate to form L- malate or the associated reverse reaction . This reaction is essential in the citric acid cycle .
There are two different classes of fumarases: Fumarases I are bacterial, iron cluster-containing, heat-labile proteins, while Fumarases II occur in prokaryotes and eukaryotes , do not require metal ions for their catalytic effect and are much more stable. Fumarases I appear as dimers, fumarases II as tetramers in the mitochondria . Lack of human fumarase II, by mutation of FH - gene to emerge and the fumaric acid Urie and tilt fibroids cause.
Individual evidence
Web links
Wikibooks: Biochemistry and Pathobiochemistry: Fumarase - Learning and Teaching Materials
