Germanium (II) selenide
| Crystal structure | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
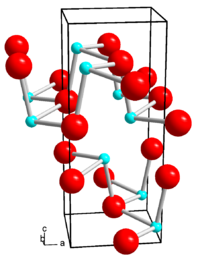
|
||||||||||||||||
| __ Ge 2+ __ Se 2− | ||||||||||||||||
| Crystal system |
orthorhombic |
|||||||||||||||
| Space group |
Pcmn (No. 62, position 4) |
|||||||||||||||
| Lattice parameters |
a = 4.38 Å , b = 3.82 Å, c = 10.79 Å |
|||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Germanium (II) selenide | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
Germanium monoselenide |
|||||||||||||||
| Ratio formula | GeSe | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
gray solid |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 151.60 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
5.6 g cm −3 (25 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
670 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
861 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Germanium (II) selenide is an inorganic chemical compound of germanium from the group of selenides .
Extraction and presentation
Germanium (II) selenide can be obtained by reacting germanium with selenium at 600 to 700 ° C and low pressure.
properties
Germanium (II) selenide is a gray solid with an orthorhombic crystal structure ( space group Pcmn (space group no. 62, position 4) , a = 4.38 Å , b = 3.82 Å, c = 10.79 Å). At low pressure it noticeably evaporates from 520–560 ° C. There is also a high-temperature form from 651 ° C with a cubic crystal structure and the space group Fm 3 m (space group no. 225) .
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g Germanium (II) selenide data sheet , 99.999% from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on January 26, 2014 ( PDF ).
- ^ A b Jean d'Ans, Ellen Lax, Roger Blachnik: Pocket book for chemists and physicists . Springer DE, 1998, ISBN 3-642-58842-5 , pp. 476 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ a b Georg Brauer (Ed.), With the collaboration of Marianne Baudler u a .: Handbook of Preparative Inorganic Chemistry. 3rd, revised edition. Volume I, Ferdinand Enke, Stuttgart 1975, ISBN 3-432-02328-6 , p. 738.
- ^ A. Okazaki: The crystal structure of germanium selenide GeSe. In: J. Phys. Soc. Yep , 13, 1958, pp. 1151-1155, doi: 10.1143 / JPSJ.13.1151 .



