Golden-eyed wood warbler
| Golden-eyed wood warbler | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Systematics | ||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
| Scientific name | ||||||||||||
| Myioborus pariae | ||||||||||||
| Phelps & Phelps Jr , 1949 |
The golden-eyed wood warbler ( Myioborus pariae ) is a small songbird from the genus Myioborus in the wood warbler family (Parulidae). The distribution area is in northeastern Venezuela . The IUCN has listed the species as "endangered" since 2000.
features
Golden-eyed wood warbler reach a body length of 13 centimeters. The wing length is 5.7 centimeters in the male, but no precise information is known in the female. Adult golden-eyed wood warbler and young birds from the first year on have a reddish brown crown plumage, the rest of the head plumage is gray and the upper side plumage is slightly olive-washed and gray. The wide yellow circles under the eyes are connected to one another by a narrow yellow band over the front of the head and thus form eye-catching glasses. Another distinctive feature are the outer white tail feathers. The wings are blackish with gray feather edges. The underside plumage is light yellow and the under tail-coverts and the rump are white. The bill and legs are also blackish. The female resembles the male, but as with the juvenile specimens , an exact description is not known.
Occurrence, nutrition and reproduction
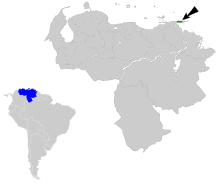
Golden-eyed wood warblers are resident birds . The distribution area is in the National Park Península de Paria and in adjacent mountain regions on the Paria peninsula in the state of Sucre in northeastern Venezuela. Individually or in pairs, they inhabit the edge areas of coffee plantations, cloud forests and humid mountain forests on the summit Cerro Azul, Cerro Patao, Cerro el Olvido and on the Cerro Humo summit, which is on the border to the national park, mostly at heights of 800 to 1150 meters. They used to occur up to a height of 650 meters. They can often be seen in the company of the sugar bird ( Coereba flaveola ) and golden-fronted vireo ( Hylophilus aurantiifrons ).
They mainly feed on insects and other invertebrates . Sometimes they lurk like flycatchers for insects flying by. There are no precise studies of the incubation and nestling times.
Hazard status and inventory figures
The IUCN has listed the species as "endangered" since 2000. The main cause is habitat destruction. The largest population is on the Cerro Humo mountain. In 1948 a single animal was sighted on Cerro Azul. The exact population number is unknown, but it is believed that golden-eyed wood warblers still occur in this area. Another single animal was seen on Cerro El Olvido in 1988 and a small group in 1999. There is also said to be a small population on Cerro Patao, but the exact number is unknown. The bird protection organization BirdLife International estimates the population size at 2500 to 10,000 individuals.
swell
literature
- Jon Curson, David Quinn, David Beadle: New World Warblers. Helm, London 1994, ISBN 0-7136-3932-6 .
Web links
- Myioborus pariae in the Red List of Threatened Species of the IUCN 2008. Posted by: BirdLife International, 2008. Accessed on 12 February, 2009.
- Golden-eyed Wood Warbler at BirdLife International