Imidocarb
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
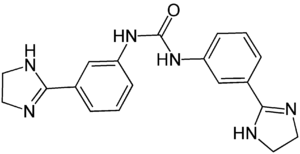
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Non-proprietary name | Imidocarb | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
1,3-bis [3- (2-imidazolin-2-yl) phenyl] urea |
||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 19 H 20 N 6 O | ||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Drug information | |||||||||||||||||||
| ATC code | |||||||||||||||||||
| Drug class | |||||||||||||||||||
| Mechanism of action |
Nucleic Acid Synthesis Inhibitors |
||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | |||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
350 ° C (decomposition) (Imidocarb dihydrochloride) |
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | |||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||||||||
Imidocarb is a drug from the group of carbanilides used in veterinary medicine , which is mainly used for the therapy and prophylaxis of babesiosis . It is mainly used as imidocarb dipropionate . The drug is not approved in human medicine.
Mechanism of action and areas of application
The exact mechanism of action has not yet been finally clarified. Imidocarb binds to the DNA of the Babesia and thus suppresses nucleic acid synthesis. It also likely inhibits polyamine synthesis. The active ingredient is only slowly metabolized and excreted in vertebrates. The half-life in the blood is about 3 hours. About 90% of the excretion takes place via the kidneys, the remaining part via the faeces.
In addition to being used against babesia , the active ingredient is suitable for the treatment of cytauxzoonosis , eperythrozoonosis , hepatozoonosis , theileriosis and canine Ehrlichiosis . In lactating animals, the drug should not be used.
Side effects
A painful swelling may develop at the injection site.
The systemic side effects are mainly due to an inhibition of cholinesterase and consist of nausea, vomiting, salivation, tremor , lacrimation, defecation and urination, colic, and serous nasal discharge. Diarrhea and shortness of breath occur rarely. These symptoms can be reduced by giving atropine .
An anaphylactic reaction occurs rarely .
Trade names
Carbesia (CH, F, I), Imizol (USA, UK, IE)
Web links
- Entry on Imidocarb at Vetpharm
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c The Merck Index. An Encyclopaedia of Chemicals, Drugs and Biologicals . 14th edition, 2006, pp. 853-854, ISBN 978-0-911910-00-1 .
- ↑ a b Registration dossier on Imidocarb stage 4 ( GHS section ) at the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), accessed on July 3, 2020.
- ↑ External identifiers or database links for imidocarbdipropionate : CAS number: 55750-06-6, EC number: 259-791-8, ECHA InfoCard: 100.054.338 , PubChem : 9983292 , ChemSpider : 8158882 , Wikidata : Q27295871 .