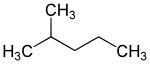
2-methylpentane
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | 2-methylpentane | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 6 H 14 | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless liquid with a faint, gasoline-like odor |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 86.18 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
liquid |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
0.65 g cm −3 |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
−154 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
60 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| Vapor pressure |
|
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Refractive index |
1.3715 (at 20 ° C, 589 nm) |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . Refractive index: Na-D line , 20 ° C | ||||||||||||||||
2-Methylpentane is a chemical compound from the group of the aliphatic , saturated hydrocarbons , more precisely the hexanes .
Extraction and presentation
2-methylpentane occurs in petroleum . The compound can also be obtained by the isomerization of n -hexane .
properties
Physical Properties
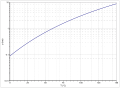
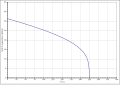
2-methylpentane is a highly flammable, volatile, colorless liquid with a faint, peculiar gasoline-like odor. According to Antoine, the vapor pressure function results from log 10 (P) = A− (B / (T + C)) (P in bar, T in K) with A = 3.9640, B = 1135.41 and C = −46.578 in the temperature range from 286 to 334 K. The temperature dependence of the enthalpy of vaporization can be calculated according to the equation Δ V H 0 = A · e (−βT r ) (1 − T r ) β (Δ V H 0 in kJ / mol, T r = (T / T c ) reduced temperature) with A = 45.25 kJ / mol, β = 0.2739 and T c = 497.5 K in the temperature range between 298 K and 333 K.
The most important thermodynamic properties are listed in the following table:
| property | Type | Value [unit] |
|---|---|---|
| Standard enthalpy of formation | Δ f H 0 gas | −174.3 kJ mol −1 |
| Enthalpy of combustion | Δ c H 0 gas | −4157.7 kJ mol −1 |
| Heat capacity | c p | 194.19 J mol −1 K −1 (25 ° C) as a liquid |
| Enthalpy of fusion | Δ f H 0 | 6.27 kJ mol −1 at the melting point |
| Entropy of fusion | Δ f S 0 | 53.43 kJ mol −1 at the melting point |
| Enthalpy of evaporation | Δ V H 0 | 27.79 kJ mol −1 at the normal pressure boiling point of 30.1 kJ mol −1 at 25 ° C |
| Critical temperature | T C | 224.5 ° C |
| Critical pressure | P C | 30.4 bar |
| Critical volume | V C | 0.368 l mol −1 |
| Critical density | ρ C | 2.72 mol·l −1 |
Vapor pressure function of 2-methylpentane
Temperature dependence of the heat of vaporization of 2-methylpentane
Safety-related parameters
2-methylpentane forms highly flammable vapor-air mixtures. The compound has a flash point of <−7 ° C. The explosion range is between 1.2% by volume (40 g / m 3 ) as the lower explosion limit (LEL) and 7% by volume (250 g / m 3 ) as the upper explosion limit (UEL). The ignition temperature is 300 ° C. The substance therefore falls into temperature class T3.
use
2-methylpentane is used as a solvent and is contained in cleaning agents. The compound is also used as a reference substance in spectroscopy and chromatography .
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n Entry on 2-methylpentane in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on April 11, 2018(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ a b Data sheet 2-methylpentane (PDF) from Merck , accessed on October 8, 2010.
- ↑ Entry on 2-methylpentane in the Classification and Labeling Inventory of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), accessed on August 1, 2016. Manufacturers or distributors can expand the harmonized classification and labeling .
- ↑ a b entry on methylpentane. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on June 16, 2014.
- ↑ Williamham, CB; Taylor, WJ; Pignocco, JM; Rossini, FD: Vapor Pressures and Boiling Points of Some Paraffin, Alkylcyclopentane, Alkylcyclohexane, and Alkylbenzene Hydrocarbons in J. Res. Natl. Bur. Stand. (US) 35 (1945) 219-244.
- ↑ a b c Majer, V .; Svoboda, V .: Enthalpies of Vaporization of Organic Compounds: A Critical Review and Data Compilation , Blackwell Scientific Publications, Oxford, 1985, p. 300.
- ↑ a b Prosen, EJ; Rossini, FD: Heats of combustion and formation of the paraffin hydrocarbons at 25 ° C in: J. Res. Natl. Bur. Stand. (US) 35 (1945) 263-267.
- ↑ Ohnishi, K .; Fujihara, I .; Murakami, S .: Thermodynamic properties of decalins mixed with hexane isomers at 298.15K. 1. Excess enthalpies and excess isobaric heat capacities in Fluid Phase Equilib. 46 (1989) 59-72, doi : 10.1016 / 0378-3812 (89) 80275-4 .
- ↑ a b Douslin, DR; Huffman, HM: Low-temperature thermal data on the five isometric hexanes in J. Am. Chem. Soc. 68 (1946) 1704-1708, doi : 10.1021 / ja01213a006 .
- ↑ a b c d Daubert, TE: Vapor-Liquid Critical Properties of Elements and Compounds. 5. Branched Alkanes and Cycloalkanes in J. Chem. Eng. Data 41 (1996) 365-372, doi : 10.1021 / je9501548 .
- ^ A b E. Brandes, W. Möller: Safety-related parameters - Volume 1: Flammable liquids and gases , Wirtschaftsverlag NW - Verlag für neue Wissenschaft GmbH, Bremerhaven 2003.