Isopulegole
The isopulegols are a group of monoterpenes that belong to the p -menthenols .
The eponymous compound isopulegol exists in two mirror-image forms, (-) - isopulegol and (+) - isopulegol.
Representative
As the representative of the isopulegols three asymmetric carbon atoms possess belong next to the Isopulegol- diastereomers and iso-isopulegol , neo-isopulegol and neoiso-isopulegol (each with its mirror-image isomers built) to the group of isopulegols.
In total there are eight stereoisomers , each two enantiomers of four different diastereomers :
- (+) - and (-) - isopulegol,
- (+) - and (-) - iso-isopulegol,
- (+) - and (-) - Neo-Isopulegol and
- (+) - and (-) - Neoiso-Isopulegol.
All eight compounds are colorless liquids.
| Isopulegole | ||||||||
| Surname | (+) - isopulegol | (-) - isopulegol | (+) - iso-isopulegol | (-) - Iso-Isopulegol | (+) - Neo-Isopulegol | (-) - Neo-Isopulegol | (+) - Neo-Iso-Isopulegol | (-) - Neo-Iso-Isopulegol |
| other names |
|
|
(1 S , 2 R , 5 R ) -2-Isopropenyl-5-methylcyclohexanol | (1 R , 2 S , 5 S ) -2-isopropenyl-5-methylcyclohexanol | (1 S , 2 S , 5 R ) -2-isopropenyl-5-methylcyclohexanol | (1 R , 2 R , 5 S ) -2-isopropenyl-5-methylcyclohexanol | (1 R , 2 R , 5 R ) -2-Isopropenyl-5-methylcyclohexanol | (1 S , 2 S , 5 S ) -2-isopropenyl-5-methylcyclohexanol |
| Structural formula |

|

|

|

|

|

|
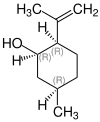
|

|
| CAS number | 104870-56-6 | 89-79-2 | 96612-21-4 | 18674-65-2 | 20549-46-6 | 144541-38-8 | ||
| 21290-09-5 (±) -neoisoisopulegol | ||||||||
| 7786-67-6 (mixture of isomers) | ||||||||
| EC number | 625-653-4 | 201-940-6 | ||||||
| (Mixture of isomers) | ||||||||
| ECHA ID | 100.154.129 | 100.001.764 | ||||||
| (Mixture of isomers) | ||||||||
| PubChem | 1268090 | 170833 | 11008146 | 6553885 | ||||
| 24585 (mixture of isomers) | ||||||||
| Wikidata object | Q27285994 | Q2103922 | ||||||
| Q54727900 (mixture of isomers) | ||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 10 H 18 O | |||||||
| Molar mass | 154.25 g mol −1 | |||||||
| Brief description | colorless liquids | |||||||
Occurrence
(+) - and (-) - isopulegol
(+) - Neo-Isopulegol
(+) - Neoisopulegol has been detected in Mentha rotundifolia ( Lamiaceae ) and is also one of the components in Eucalyptus citriodora oil .
(+) - Neoiso-isopulegol
(+) - Neoiso-isopulegol was first isolated in 1960 from the mint oil of round-leaved mint ( Mentha rotundifolia ).
Natural extraction and synthesis
Natural extraction
Isopulegol can be obtained from a wide variety of plants, for example from the essential oils of Eucalyptus citriodora or lemongrass .
synthesis
It was first named in 1896 by Ferdinand Tiemann and R. Schmidt during the systematic investigation of the reactions of citronellal : "A cyclic alcohol, which we temporarily call isopulegol, is obtained from citronellal under the following conditions ..."
The substance can be obtained synthetically by catalytic cyclization (intramolecular Prins reaction of citronellal , also called intramolecular carbonyl-ene reaction). By choosing a suitable catalyst , the selectivity of the reaction for one or more stereoisomers of isopulegol can be increased. Typical catalysts are Lewis acids based on aluminum or silicon compounds , including zeolites such as clinoptilolite .
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b entry on p-menthenols. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on June 7, 2016.
- ↑ Entry on eucalyptus oils. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on June 7, 2016.
- ↑ Sumio Shimizua, Nagamori Ikedaa and Hiroo Uedaa: Isolation of (+) - Neoiso-isopulegol, a New Stereoisomer of Isopulegol and Piperitenone from a Variety of Mentha rotundifolia , Bull. Of the Agricult. Chem. Soc. Japan, Vol. 24, No. 3 (1960); doi : 10.1080 / 03758397.1960.10857672 .
- ^ BR Rajeswara Rao, PN Kaul, KV Syamasundar, S. Ramesh: Comparative composition of decanted and recovered essential oils of Eucalyptus citriodora Hook . In: Flavor and Fragrance Journal . tape 18 , no. 2 , 2003, p. 133-135 , doi : 10.1002 / ffj.1157 .
- ^ Raquel G. Jacob et al .: Green synthesis of ( -) - isopulegol from (+) - citronellal: application to essential oil of citronella . In: Tetrahedron Letters . tape 44 , no. 18 , 2003, p. 3605-3608 , doi : 10.1016 / S0040-4039 (03) 00714-7 .
- ↑ The specified conditions were: heating citronellal with acetic anhydride and subsequent saponification of the acetic ester purified by distillation. The structure of Pulegol is given in the article as the structure for this "Isopulegol" .
- ↑ Ferdinand Tiemann and R. Schmidt: About the connections of the citronellal series . In: Reports . tape 29 , no. 1 , January 1896, p. 903-926 , doi : 10.1002 / cber.189602901175 ( PDF ).
- ↑ US Patent 2117463: Method of producing isopulegol of May 17, 1938 to Charles O. Terwilliger
- ↑ Kelly A. da Silva et al .: Cyclization of (+) - citronellal to (-) - isopulegol catalyzed by H 3 PW 12 O 40 / SiO 2 , Catalysis Communications Vol. 5 No. 8 (2004), p. 425 -429; doi: 10.1016 / j.catcom.2004.05.001 .
- ↑ Mercedes Fuentes et al .: Cyclization of Citronellal to Isopulegol by Zeolite Catalysis , Applied Catalysis, vol. 47 no. 2, pp. 367-374 (1989); doi: 10.1016 / S0166-9834 (00) 83242-X .

