JWH-073
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
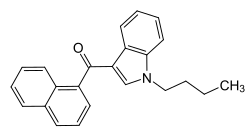
|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | JWH-073 | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 23 H 21 NO | |||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| Drug information | ||||||||||||||||
| Drug class | ||||||||||||||||
| Mechanism of action | ||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 327.42 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
JWH-073 is a synthetic chemical compound from the group of alkyl indole - derivatives and was designed by John W. Huffman developed. It acts as a partial agonist on CB 1 and with about 5-fold higher selectivity on the CB 2 receptor. Among other things, it shows analgesic properties.
This cannabinoid was found as an added active ingredient in products that were sold by the manufacturers as “herbal mixtures” under the name “ Spice ” or in similar products. According to the expert committee for narcotics in Germany, JWH-073 has a stronger effect than THC .
Legal position
- Germany:
- As an active ingredient , JWH-073 was classified in Germany as a marketable but not a prescription narcotic by entry in Annex II of the Narcotics Act (BtMG) as of January 22, 2010 . On January 14, 2015, the German Federal Supreme Court ruled on the not insignificant amount of various synthetic cannabinoids . The limit of the not small amount was set at six grams for the cannabinoids JWH-073 and CP 47,497.
- Switzerland:
- With the entry into force of the revised Narcotics Ordinance by Swissmedic on December 1, 2010, JWH-073 was made subject to the Narcotics Act and has therefore been illegal since then. Importation, possession, distribution etc. are punished according to the Narcotics Act.
- Sweden and Lithuania:
- JWH-073 has been classified as an intoxicant in Sweden and Lithuania .
See also
Individual evidence
- ↑ There is not yet a harmonized classification for this substance . A label of [No public or meaningful name is available] in the Classification and Labeling Inventory of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), retrieved on November 11, 2019, is reproduced from a self-classification by the distributor .
- ↑ Aung MM, Griffin G, Huffman JW, et al. : Influence of the N-1 alkyl chain length of cannabimimetic indoles upon CB 1 and CB 2 receptor binding . In: Drug Alcohol Depend . 60, No. 2, August 2000, pp. 133-40. doi : 10.1016 / S0376-8716 (99) 00152-0 . PMID 10940540 .
- ↑ Federal Law Gazette 2009 I p. 3944
- ↑ Federal Institute for Drugs and Medical Devices (BfArM): Committee of Experts for Narcotics according to Section 1, Paragraph 2 of the BtMG. ( Memento of December 30, 2014 in the Internet Archive ) As of August 26, 2009, accessed on September 27, 2010.
- ↑ Federal Institute for Drugs and Medical Devices (BfArM): [ Narcotics. ] As of June 1, 2010, accessed on September 27, 2010.
- ↑ BGH, judgment of January 14, 2015 - 1 StR 302/13
- ↑ Juris.de: Legal Highs - Limits for synthetic cannabinoids set , accessed on January 24, 2015.
- ↑ Ordinance of the Swiss Agency for Therapeutic Products on Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances (Narcotics Ordinance Swissmedic, BetmV-Swissmedic.) Amendment of 10 September 2010 (PDF; 590 kB) Comes into force on 1 December 2010.
- ↑ Federal Act on Narcotics and Psychotropic Substances (Narcotics Act, BetmG) of October 3, 1951 (as of January 1, 2010) (PDF; 183 kB). Swiss Narcotics Act, relevant criminal provisions: Art. 19 and following.
- ↑ European Monitoring Center for Drugs and Drug Addiction (EMCDDA): Synthetic Cannabinoids and Spice , accessed September 27, 2010.

