Jasmonic acid methyl ester
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
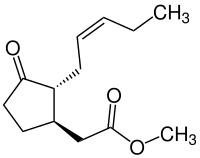
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Structural formula of (-) - jasmonic acid methyl ester | |||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Jasmonic acid methyl ester | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 13 H 20 O 3 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless, oily liquid with a floral odor |
||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 224.3 g · mol -1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
liquid |
||||||||||||||||||
| density |
1.03 g cm −3 |
||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point | |||||||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
302-303 ° C |
||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
almost insoluble in water, soluble in ethanol |
||||||||||||||||||
| Refractive index |
1.474 (20 ° C) |
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . Refractive index: Na-D line , 20 ° C | |||||||||||||||||||
Jasmonic acid methyl ester ( methyl jasmonate ) is the methyl ester of jasmonic acid and, like the latter, a phytohormone .
Isomers
There are two chiral carbon atoms in the methyl jasmonate molecule . Each can take either the R or S configuration, so there are four isomers.
- (-) - Jasmonic acid methyl ester [(1 R , 2 R ) -isomer, CAS number 1211-29-6]
- (+) - Jasmonic acid methyl ester [(1 S , 2 S ) -isomer, CAS number 78609-06-0]
The racemic mixture, (+/-) - jasmonic acid methyl ester, is defined by CAS number 20073-13-6. There are also the two epi -jasmonic acid methyl esters:
- (-) - epi -jasmonic acid methyl ester [(1 S , 2 R ) -isomer]
- (+) - epi -jasmonic acid methyl ester [(1 R , 2 S ) -isomer, CAS number 95722-42-2]
The undefined mixture of all isomers is described by CAS number 1101843-02-0.
(+) - epi -jasmonic acid methyl ester has the strongest odor of the isomers, which shows the importance of this form for the adaptation of the receptors and the activation of the sensory response.
Occurrence
Jasmonic acid methyl ester is an ingredient ubiquitous in the plant kingdom . It is part of jasmine oil .
synthesis
The precursor of jasmonic acid methyl ester is jasmonic acid , which is methylated at the first carbon atom by the enzyme jasmonate methyl transferase .
effect
Jasmonic acid methyl ester has a very broad spectrum of activity that is largely congruent with jasmonic acid: growth inhibition, participation in senescence , formation of so-called jasmonate-induced proteins (JIP) and protease inhibitors . The latter are part of the plant's defense mechanism against herbivores , which cause jasmonates to be released through feeding-related mechanical damage to the plant. The formation of secondary plant substances ( phytoalexins , for example with an antibiotic effect) is stimulated by jasmonate ( elicitor ) and is the answer to damage caused by pathogenic microorganisms.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d thegoodscentscompany.com: methyl jasmonate , accessed June 4, 2018.
- ↑ Duchefa: MSDS
- ↑ a b c data sheet methyl jasmonate from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on April 10, 2011 ( PDF ).
- ↑ External identifiers or database links for (+) - jasmonic acid methyl ester : CAS number: 78609-06-0, PubChem : 6427970 , ChemSpider : 4933379 , Wikidata : Q27109876 .
- ↑ External identifiers of or database links to (+) - epi-jasmonic acid methyl ester : CAS number: 95722-42-2, PubChem : 12566815 , Wikidata : Q54806830 .
- ↑ a b Methyl Jasmonate - MOTM September 2001
- ↑ G. Sembdner, B. Parthier: The Biochemistry and the Physiological and Molecular Actions of Jasmonates , in: Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. Plant Mol. Biol. 44: 569-589 (1993).
- ↑ AR Menhaj, SK Mishra, S. Bezhani, K. Klopp piercing: posttranscriptional control in the expression of the genes coding for high-light-regulated HL # 2 proteins in Planta 209 (1999), pp 406-413.
- ^ R. Halitschke, IT Baldwin: Jasmonates and Related Compounds in Plant-Insect Interactions , in: Journal of Plant Growth Regulation 23 (2004), pp. 238–245.
