Potassium molybdate
| Crystal structure | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
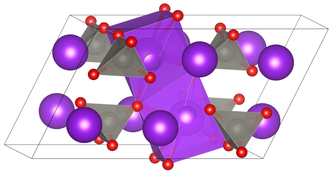
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| __ K + __ Mon 6+ __ O 2− | |||||||||||||||||||
| Crystal system |
monoclinic |
||||||||||||||||||
| Space group |
C 2 / m (No. 12) |
||||||||||||||||||
| Lattice parameters |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Potassium molybdate | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
Dipotassium molybdate |
||||||||||||||||||
| Ratio formula | K 2 MoO 4 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless solid |
||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 238.13 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||||||||||||||
| density |
2.34 g cm −3 |
||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
919 ° C |
||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
soluble in water (646 g l −1 at 25 ° C) |
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||||||||
Potassium molybdate is an inorganic chemical compound of potassium from the group of molybdates .
Extraction and presentation
Potassium molybdate can be obtained by reacting an aqueous solution of potassium hydroxide with ammonium heptamolybdate .
properties
Potassium molybdate is a colorless solid. It has a monoclinic crystal structure with the space group C 2 / m (space group no. 12) isomorphic to potassium tungstate . At higher temperatures or pressures, a phase change to another structure takes place.
use
Potassium molybdate is used in chemical research and studied as a dietary supplement.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b B. M. Gatehouse, P. Leverett: Crystal structure of potassium molybdate, K2MoO4. In: Journal of the Chemical Society A: Inorganic, Physical, Theoretical. 1969, p. 849, doi : 10.1039 / J19690000849 .
- ↑ a b c d e data sheet Potassium molybdate, 98% from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on June 12, 2019 ( PDF ).
- ↑ a b c Dale L. Perry: Handbook of Inorganic Compounds . CRC Press, 2016, ISBN 978-1-4398-1462-8 , pp. 328 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ a b Michio Inagaki, Yasuo Nishikawa, Motosugu Sakai: Synthesis and phase transitions of K2MoO4. In: Journal of Materials Chemistry. 2, 1992, p. 323, doi : 10.1039 / JM9920200323 .
- ↑ FXNM Kools, AS Koster, GD Rieck: The Structures of Potassium, Rubidium and Cesium Molybdate and Tungstate . In: Acta Cryst. B26, 1970, p. 19741-1977 , doi : 10.1107 / S0567740870005277 .
- ^ AJ van den Berg, H. Overeijnder, F. Tuinstra: The average structure of K2MoO4 in the incommensurate phase at 633 K. In: Acta Crystallographica Section C Crystal Structure Communications. 39, p. 678, doi : 10.1107 / S0108270183005909 .
- ↑ W. Paraguassu, GD Saraiva, S. Guerini, PTC Freire, BTO Abagaro, J. Mendes Filho: Pressure-induced phase transition on K2MoO4: A Raman scattering study and ab initio calculations. In: Journal of Solid State Chemistry. 196, 2012, p. 197, doi : 10.1016 / j.jssc.2012.06.021 .
- ↑ Data sheet Potassium molybdenum oxide, anhydrous, 99.8% (metals basis) from AlfaAesar, accessed on June 12, 2019 ( PDF )(JavaScript required) .