Molybdic acid
| Crystal structure | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||||||||||||
|
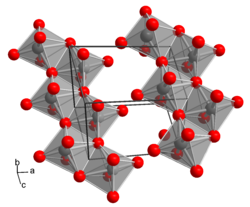
__ Mo 6+ __ O 2− crystal structure of H 2 MoO 4 |
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Molybdic acid | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
Molybdenum (VI) acid |
|||||||||||||||
| Ratio formula | MoO 3 · H 2 O | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless (triclinic) or yellow (monoclinic) solid |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 161.95 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
300 ° C (85%) |
|||||||||||||||
| pK s value |
|
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
0.5 g l −1 (monohydrate, 15 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Molybdic acid has the empirical formula H 2 MoO 4 and can be used as monohydrate of molybdenum trioxide be construed: MoO 3 · H 2 O. In contrast about the seemingly analogue construction of sulfuric acid (H 2 SO 4 ), there are no discrete H 2 MoO 4 - molecules , instead, is molybdic acid of a layer lattice of MoO 6 - octahedra (yellow, monoclinic form) or zig-zag chains of MoO 6 octahedra (colorless, triclinic form). The conjugate base of molybdic acid MoO 4 2− is called molybdate , the salts of molybdic acid are called molybdates . Like the sulfate ions , the molybdate ions consist of MoO 4 2− tetrahedra.
Molybdate (MoO 4 2− ) is the bioavailable form of molybdenum , that is, it can be used by living things .
Molybdic acid can be obtained as a white precipitate if a molybdate solution is acidified. Nitric acid molybdate solutions can also deposit the yellow hydrate of molybdic acid H 2 MoO 4 · H 2 O in crystalline form if left standing for a long time .
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e A. F. Holleman , E. Wiberg , N. Wiberg : Textbook of Inorganic Chemistry . 101st edition. Walter de Gruyter, Berlin 1995, ISBN 3-11-012641-9 .
- ↑ a b c Datasheet Molybdic acid about 85% MoO 3 , contains ammonium molybdate (PDF) from Merck , accessed on April 11, 2011.
- ^ D'Ans-Lax: Taschenbuch für Chemiker und Physiker , 4th edition, Volume 3, Springer Verlag 1998, ISBN 3-540-60035-3 .
- ^ Schwarz G. et al .: Molybdenum cofactors, enzymes and pathways . In: Nature . 460, No. 7257, 2009, pp. 839-847. PMID 19675644 .
- ↑ Jander-Blasius, Textbook of analytical and preparative inorganic chemistry, 8th edition, S. Hirzel Verlag, Stuttgart 1969.

