Lake Ladoga
| Lake Ladoga | ||
|---|---|---|
|
||
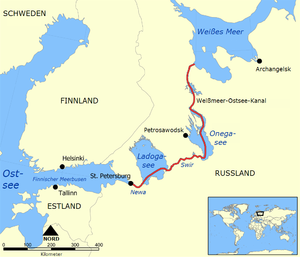
| Location of Lake Ladoga with the White Sea-Baltic Sea Canal | ||
| Geographical location | Leningrad Oblast , Republic of Karelia ( Russia ) | |
| Tributaries | Swir , Volkhov , Vuoksi , Jänisjoki , Tohmajoki , Sjas | |
| Drain | Neva | |
| Islands | Valaam | |
| Places on the shore | Sortavala , Syasstroi | |
| Location close to the shore | St. Petersburg | |
| Data | ||
| Coordinates | 60 ° 49 ′ N , 31 ° 32 ′ E | |
|
|
||
| Altitude above sea level | 4 m | |
| surface | 17,700 km² | |
| length | 219 km | |
| width | 83 km | |
| volume | 908 km³ | |
| Maximum depth | 230 m | |
| Middle deep | 51 m | |
| Catchment area | 281,000 km² | |
|
particularities |
largest lake in Europe |
|
The Lake Ladoga ( Russian Ладожское Озеро / Ladoschskoje Ozero , Finnish Laatokka , formerly Nevajärvi , Karelian Luadogu , Vepsian Ladoganjärv ) has approximately 18,000 sq km of the largest lake in Europe. It is located in northwestern Russia between Leningrad Oblast and the south of the Republic of Karelia , near the border with Finland .
The Valaam Monastery , a Russian Orthodox monastery, is located on the island of Valaam .
Geography and geology
Lake Ladoga is a freshwater lake, the water level of which is only a few meters above sea level. Its water surface is about 17,700 km² , together with its well over 500 islands it covers 18,135 km². The lake extends in north-south direction for almost 220 km, measures in west-east direction up to 120 km and is at least 80 km wide. The maximum depth of Lake Ladoga is 225 m, the average depth is around 52 m.
The lake is geologically very young. Like almost all lakes in northern Europe, it was created by the excavation activity of the Ice Age inland ice. It was not until the end of the Vistula Ice Age that the lake basin formed around 15,000 years ago when the glacier melted back.
Lake Ladoga is connected to the Baltic Sea via its outlet, the Neva River . There is a connection to Lake Onega via the Swir , one of the main tributaries of the Ladoga . From there, on the one hand, there are navigable waterways to the White Sea with the White Sea-Baltic Sea Canal and the Northern Dvina ; on the other hand, the canals of the Volga-Baltic Sea Waterway provide access to the Caspian and Black Sea . Here, the Ladoga lake between the confluence of the Swir and the outflow of the Neva is bypassed through the Ladoga Canal .
The catchment area of Lake Ladoga, which is frozen over from around the end of November to the beginning of April, covers 280,336 km².
history
Until the 13th century, the lake was still called Newo , then it was named after the medieval trading town of Staraya Ladoga in Lake Ladoga on its south bank (see Old Ladoga ).
In 1809, with the cession of Finland, which had previously belonged to Sweden , the northwestern part (about half) of the lake came to Russia as part of the province of Finland. This part of the lake, with the attainment of independence of Finland had become Finnish in 1918, came to the end of the Soviet-Finnish Winter War of 1940 by the Treaty of Moscow to the territory of the Soviet Union .
During the Second World War , Leningrad, besieged by the Germans, was supplied via the frozen Lake Ladoga (the road of life ). The three Ladoga battles for the opening of the land route to Leningrad took place south of the lake from 1942 to 1943 .
fauna
In the lake lives Phoca hispida ladogensis , a subspecies of the ringed seal ( Phoca hispida ). It is one of two subspecies of the ringed seal that live in freshwater.
See also
Web links
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g Article Lake Ladoga in the Great Soviet Encyclopedia (BSE) , 3rd edition 1969–1978 (Russian)
- ↑ a b Lake Ladoga in the State Water Directory of the Russian Federation (Russian)