laryngitis
| Classification according to ICD-10 | |
|---|---|
| J04.0 | Acute laryngitis |
| J04.2 | Acute laryngotracheitis |
| J05.0 | Acute obstructive laryngitis (croup) and epiglottitis |
| J06.0 | Acute laryngopharyngitis |
| J37.0 | Chronic laryngitis |
| J37.1 | Chronic laryngotracheitis |
| ICD-10 online (WHO version 2019) | |
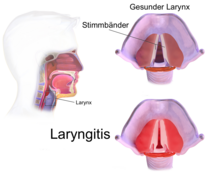
Under a laryngitis (from ancient Greek λάρυγξ laryngeal , throat 'and the ending -itis for inflammatory disease) refers to an inflammation of the larynx . The main symptom of laryngitis (formerly also known as larynx catarrh ) is hoarseness ( raucedo ) with dysphonia up to aphonia , often accompanied by a dry, excruciating cough . Other symptoms can include a severe sore throat and a fever of up to 40 ° C.
Classification
Laryngitis can be divided into an acute, a chronic and a phlegmonous form.
Acute laryngitis
The acute form of laryngitis is divided into inflammation of the various levels of the larynx (supraglottis, glottis , subglottis), but especially the vocal folds (glottis). Subglottic laryngitis is also known as pseudocroup . The upper part of the windpipe is also very often involved; then it is referred to as laryngotracheitis .
Acute laryngitis is mainly caused by viral infections of the upper respiratory tract or, rarely, by strong voice strain in rooms with dry, possibly smoky air.
Chronic laryngitis
Laryngitis is considered chronic if the inflammation lasts for more than three weeks. In combination with an inflammation of the lining of the throat ( pharyngitis ) it occurs as laryngopharyngitis .
Chronic laryngitis develops
- from acute laryngitis with insufficient sparing of the voice,
- by smoking and working in a dusty, dry environment,
- through alcohol abuse,
- due to reflux of gastric juice, see Laryngitis gastrica ,
- with constant mouth breathing with impaired nasal breathing,
- in the context of ascending infections ( bronchitis with constant coughing),
- rarely with incorrect vocal technique or as a result of long-standing functional voice disorder.
Chronic laryngitis must always be monitored, as the transition from chronic inflammation to precancerous disease (and thus possibly further to carcinoma ) is often fluid. If only one vocal cord is reddened, vocal cord cancer or tuberculosis should be considered.
Phlegmonous laryngitis
Phlegmonous laryngitis is extremely rare, but it is life-threatening. The cause can be reduced immunity , trauma or severe infectious diseases that can spread from neighboring structures, such as a tongue base abscess or a peritonsillar phlegmon . In this form of laryngitis, the muscle layer of the larynx , the tela submucosa , the perichondrium, and the ligaments are affected. Symptoms are high fever, severe pain when swallowing and, in particular, respiratory failure ( suffocation ) due to the larynx edema, which can occur surprisingly quickly and requires immediate therapy. Perichondritis of the larynx can also develop as a result of syphilis , typhus , tuberculosis or carcinoma , but also with diphtheria , influenza and mechanical injuries . Must be distinguished is the epiglottitis .
therapy
Therapy of acute laryngitis
In addition to treating an underlying disease and eliminating the noxious substances involved (e.g. tobacco smoke), the focus is on protecting the voice in acute laryngitis. It is beneficial to temporarily completely forego the use of the voice - at best speak softly, carefully with a lowered voice. Whispering should be strictly avoided because the maximum tension of the vocal folds required for this causes considerable stress. Hot neck envelopes and hot drinks as well as steam inhalations with essential oils , for example from the Chamomile or sage leaves have a soothing effect, in liquid extracts no alcohol should be added, as this dries the larynx, which is undesirable. In the event of swelling of the vocal folds , inhalations containing hydrocortisone can have a supportive effect; antibiotics are given for secondary infections with pus formation . If there is an urge to cough, the symptoms are treated.
A complication of acute laryngitis is inflammation of the vocalis muscle , which can lead to insufficient closure of the vocal folds .
Therapy of chronic laryngitis
Tobacco, alcohol and hot spices should be avoided in chronic laryngitis; proton pump inhibitors are the drug of choice for reflux . The dry mucous membranes are moistened by inhalation, decongestant drugs should not be used. If necessary, nasal breathing should be improved through surgical measures or correct voice technique learned through voice therapy.
Therapy of phlegmonous laryngitis
In the case of edema of the larynx during phlegmonous processes, which can lead to severe shortness of breath, a calcium-vitamin C treatment is first carried out, which is supplemented with ice cuffs around the neck, which often causes sufficient swelling. If necessary, this is supplemented by an intravenous administration of a glucocorticoid , which helps to avoid the ultima ratio : If conventional endotracheal intubation with the thinnest possible tube is no longer possible when there is a risk of complete closure of the airways , a tracheotomy or cricothyrotomy ( tracheotomy ) is performed.
See also
literature
- Hans-Georg Boenninghaus : Ear, nose and throat medicine for students of medicine . 10th edition. Springer, Berlin / Heidelberg / New York 1996, ISBN 3-540-60396-4 , pp. 325-329 .
Individual evidence
- ↑ Treatment of laryngitis in children - the principles of therapy. Medicine Power. Retrieved October 22, 2017.
- ↑ a b Otto Körner, Otto Steurer: Textbook of ear, nose, throat and larynx diseases . Springer-Verlag, March 8, 2013, ISBN 978-3-642-99294-0 , pp. 459-461.
- ^ Norbert Roewer, Holger Thiel: Pocket atlas of anesthesia: color tables by Jürgen Wirth . Georg Thieme Verlag, April 14, 2010, ISBN 978-3-13-154364-6 , p. 280.