Lithium sulfide
| Crystal structure | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||||||||||||
| __ Li + __ S 2− | ||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Lithium sulfide | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Ratio formula | Li 2 S | |||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 45.95 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
1.64 g cm −3 |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
1372 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
Reacts violently with water |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Lithium sulphide is a sulphide of lithium and has the empirical formula Li 2 S.
properties
It is a colorless solid that crystallizes in an antifluorite structure . Lithium sulfide is so hygroscopic that it dissolves in air . It reacts violently with water, forming an alkaline solution:
The hydrogen sulfide formed with water, which is in equilibrium with hydrogen sulfide , gives lithium sulfide a sulphurous smell, like rotten eggs.
Lithium sulfide is flammable.
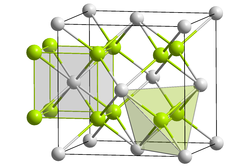
Lithium sulfide crystallizes - like sodium oxide Na 2 O - in the antifluorite structure, i. That is, each lithium ion is tetrahedrally surrounded by four sulfide ions, each sulfide ion is cubically surrounded by eight cations.
Manufacturing
Lithium sulfide can be obtained in good purity from the elements by using liquid ammonia at −33 ° C as a solvent:
or.
This overall reaction also takes place when a lithium-sulfur accumulator is completely discharged .
Lithium sulfide can also be obtained in its pure form if lithium hydrogen sulfide is heated to 150 ° C in a vacuum:
Possible occurrence in future accumulators
Intensive work is being carried out on the development of a lithium-sulfur battery . When fully discharged, it contains lithium sulfide, which is converted back into sulfur when charged. Since lithium sulfide Li 2 S is hardly soluble in the organic solvents that are commonly used in lithium cells, it exists as a solid substance.
Research is being carried out into the use of lithium sulfide as a component of solid electrolytes . With the help of these solid electrolytes, accumulators can be produced that do not require liquid, which z. B. at elevated temperatures or miniaturized batteries can be advantageous.
Individual evidence
- ^ A b David R. Lide: CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, 85th Ed., CRC Press LLC 2005.
- ↑ a b c data sheet lithium sulfide at AlfaAesar, accessed on 08/24/2020 ( PDF )(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ P. Pandit, B. Rakshit, SP Sanyal: Electronic and elastic properties of alkali metal sulphides-Li 2 S and Na 2 S . In: Indian Journal of Pure & Appl. Phys. tape 47 , 2009, p. 804-807 .
- ^ FW Bergstrom: The Polysulfides and Polyselenides of Lithium, Sodium and Potassium . In: Journal of the American Chemical Society . tape 48 , no. 1 , 1926, pp. 146–151 , doi : 10.1021 / ja01412a021 .
- ↑ Robert Juza , Wilhelm Uphof: On the knowledge of lithium sulfide . In: Journal of Inorganic and General Chemistry . tape 287 , no. 3 , 1956, pp. 113-119 , doi : 10.1002 / zaac.19562870302 .
- ↑ a b N. V. Arkhipova, LD Leont'eva, AM Mikhailova: Ionic Lithium-Conducting Solid Li2S – Sb2Sx Electrolytes . In: Russian Journal of Electrochemistry . tape 39 , no. 5 , 2003, p. 588-590 , doi : 10.1023 / A: 1023829010924 .
- ↑ Masahiro Tatsumisago, Hideki Yamashita, Akitoshi Hayashi, Hideyuki Morimoto, Tsutomu Minami: Preparation and structure of amorphous solid electrolytes based on lithium sulfide . In: Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids . tape 274 , 2000, pp. 30-38 , doi : 10.1016 / S0022-3093 (00) 00180-0 .


![{\ displaystyle {\ ce {Li2S + 8H2O -> 2 [Li (H2O) 4] + + S ^ {2-}}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/756047bac7a2b0639bf576c95d6abff5258d2b47)



