Investment rate
The investment ratio is a business and economic indicator that the share of expenditure Gross fixed capital formation in fixed assets of a company or on the gross domestic product (or national income ) of a state reproduces.
General
Private households , companies and the state with its state-owned companies come into question as investors . The investment rate affects all types of investment, i.e. expansion , replacement or rationalization investments . In the case of companies, investments also include intangible investments ( research and development ). Your key figure is the research quota (R&D quota).
Investment activity is of paramount importance for the sustainable economic growth of a country or the competitiveness of a company. The investment quota as a measure for determining the economic attractiveness of an economy enables international location comparisons and reveals weaknesses for sustainable growth. The investment rate provides information about investment activity in a company or in an economy. High investment activity is an indication of expected or existing increases in demand or technological progress , low investment activity leads to an investment backlog . The higher the investment rate, the higher the per capita income and vice versa.
detection
The determination is based on various economic parameters, depending on whether the key figure is economic or business.
National economy
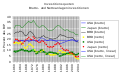
Investment rates in the triad
The macroeconomic investment quota results from the comparison of the gross capital investments with the gross domestic product or national income :
- .
The marginal investment rate is the derivation of this investment rate. It shows how much the investments change if the income changes by one unit:
- .
In a linear investment function
is the marginal investment rate . In this investment function, investments are a function of national income; they change in the same direction as national economic income. The Keynesian consumption function is specified similarly . Often, however, the investment function is specified differently from the consumption function according to the accelerator principle; the investments then do not change in the same direction as the total income, but like the change in the total income. The marginal consumption rate and the marginal saving rate can be defined analogously for consumption and saving .
The growth rate of an economy results from the quotient of the investment rate and the marginal capital coefficient :
- .
The economic research quota can be calculated from the total research and development expenditure and the gross national product :
- .
Research and development expenditure is made up of government research expenditure (especially at universities and academies , research funding ) and the research and development costs of companies. If the research quota increases for a given gross national product, the research intensity of a state has improved.
Business administration
In the business investment rate , the gross investments in fixed assets are the revenues compared:
- .
The investment rate is usually the highest in asset-intensive companies.
In the case of companies, investments also include intangible investments ( research and development ). Your key figure is the research quota (R&D quota). The research quota results from the comparison of the research and development costs with the sales revenues:
- .
A high research quota have research-intensive companies in the high technology (such as the pharmaceutical industry , electronics industry , radio and communications engineering , aircraft or weaponry on).
statistics
The investment rate is an indication of the willingness to invest on the part of economic agents. In terms of government investment ratios, Ireland led in 2016 with 35.7% , followed by Turkey (29.3%), Norway (25.3%) and the Czech Republic (24.9%). At 20.9%, Germany was just above the EU-28 median of 19.9%. The investment quota decreased for German companies. While the net investment rate was 9.2% in 1992, it has fallen continuously over the years to 2.6% (2017). In 2016, South Korea (4.23%) led the world in research rates, followed by Japan (3.29%), Sweden (3.25%), Austria (3.09%), Germany (2.94%), Denmark ( 2.87%) or USA (2.79%).
See also
Web link
- Investment rates of non-financial corporations in the euro area by country 2006–2016 at Eurostat
Individual evidence
- ↑ Georg Milbradt / Gernot Nerb / Wolfgang Ochel / Hans-Werner Sinn, The Ifo Business Compass: Numbers - Facts - Background , 2011, p. 14
- ↑ Jörg Arnsmeyer, Fundamentals of Economics , 2018, p. 100
- ↑ Manfred Neumann, in: Economic and growth policy, in: Springer Fachmedien GmbH (Hrsg.), Handwörterbuch der Volkswirtschaft , 1978, p. 605 f.
- ↑ WKO Statistics, November 2018
- ↑ Federal Statistical Office of November 30, 2018, National Accounts , p. 11
- ↑ Kleine Zeitung of December 1, 2017, Austria in second place for research quota EU-wide