Whale heads
| Whale heads | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||||||||
| Systematics | ||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
| Scientific name | ||||||||||||
| Cetomimidae | ||||||||||||
| Goode & Bean , 1895 |
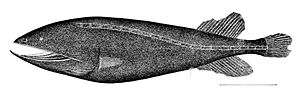
The whale heads (Cetomimidae; Greek ketos "whale", mimos "imitator") are a family of deep-sea fish . They are widespread in the seas of the southern hemisphere, reaching a depth of 3500 meters.
features
Whale heads stand out because of their large, deeply split mouth and are often deep red or orange in color. Light of this wavelength is already filtered out in the upper water layers, so that it appears deep black in the depths. Dorsal and anal fin located far back on the body, lack pelvic fins. The animals do not have a swim bladder . Adapted to life at great depths, the fish have only very small eyes, but a very well developed lateral line organ . Their loose, unscaled skin and the lack of luminous organs distinguish them from the other whale-head species . The largest species, Gyrinomimus grahami , reaches a length of 39 centimeters.
There is such a strong sexual dimorphism between the females and males of the whale heads that the males have been described as an independent fish family called "Megalomycteridae". Males are a maximum of 3.5 centimeters long. In addition, the larvae of the Cetomimidae deviate so much anatomically from the adult animals that a fish family of their own was established for them, the mirapinnidae . So were z. B. the males of Cetostoma regani as " Cetomimoides parri ", the larvae as " Parataeniophorus gulosus ". The connections were only recognized in 2009.
Way of life
Whale heads feed on all kinds of crustaceans. Their stomachs are extremely elastic, so that they can swallow larger prey. Since the males' sole purpose is to deliver sperm, growing larger than this is not worth it. The females, on the other hand, grow larger in order to produce as many egg cells as possible. Like many deep-sea fish, the whale heads take part in a vertical hike during the day. Every evening they hike in layers of water above 700 meters, only to disappear back into the depths at dawn. Young animals seem to prefer shallower water.
Systematics
There are 26 species in 14 genera.

-
Ataxolepis
- Ataxolepis apus Myers & Freihofer, 1966 .
- Ataxolepis henactis Goodyear, 1970 .
-
Cetichthys
- Cetichthys indagator (Rofen, 1959) .
- Cetichthys parini Paxton, 1989 .
-
Cetomimus
- Cetomimus compunctus Abe, Marumo & Kawaguchi, 1965 .
- Cetomimus craneae Harry, 1952 .
- Cetomimus gillii Goode & Bean , 1895 .
- Cetomimus hempeli Maul, 1969 .
- Cetichthys indagator (Rofen 1959) .
- Cetomimus kerdops Parr, 1934 .
- Cetomimus picklei (Gilchrist, 1922) .
- Cetomimus teevani Harry, 1952 .
-
Cetostoma
- Cetostoma regani Zugmayer, 1914 .
-
Danacetichthys
- Danacetichthys galathenus Paxton, 1989 .
-
Ditropichthys
- Ditropichthys storeri ( Goode & Bean , 1895) .
-
Eutaeniophorus
- Eutaeniophorus festivus (Bertelsen & Marshall 1956) .
-
Gyrinomimus
- Gyrinomimus andriashevi Fedorov, Balushkin & Trunov, 1987 .
- Gyrinomimus bruuni Rofen, 1959 .
- Gyrinomimus grahami Richardson & Garrick, 1964 .
- Gyrinomimus myersi Parr, 1934 .
- Gyrinomimus parri Bigelow 1961 .
-
Megalomycter
- Megalomycter teevani Myers & Freihofer 1966 .
-
Mirapinna
- Mirapinna esau Bertelsen & Marshall, 1956 .
-
Notocetichthys
- Notocetichthys trunovi Balushkin, Fedorov & Paxton, 1989 .
-
Parataeniophorus Bertelsen & Marshall, 1956
- Parataeniophorus brevis Bertelsen & Marshall 1956 .
-
Rhamphocetichthys
- Rhamphocetichthys savagei Paxton, 1989 .
-
Vitiaziella
- Vitiaziella cubiceps breed 1955 .
swell
literature
- Joseph S. Nelson : Fishes of the World , John Wiley & Sons, 2006, ISBN 0-471-25031-7
Individual evidence
- ↑ Daniel Lingenhöhl: Make one out of three, revealed extreme gender differences in the deep sea . Article at Wissenschaft-online.de from January 21, 2009.
- ↑ G. David Johnson, John R. Paxton, Tracey T. Sutton, Takashi P. Satoh, Tetsuya Sado, Mutsumi Nishida & Masaki Miya: Deep-sea mystery solved: astonishing larval transformations and extreme sexual dimorphism unite three fish families. Biol. Lett. 23 April 2009 vol. 5 no. 2 235-239 doi : 10.1098 / rsbl.2008.0722
Web links
- Whale heads on Fishbase.org (English)

