Methylenediphenyl isocyanate
Methylenedi (phenyl isocyanate) s ( MDI ) are chemical compounds from the group of aromatic isocyanates . Methylenedi (phenyl isocyanate) s normally represent a mixture of several constitutional isomers which differ in the position of the isocyanate groups. It is in the form of a colorless to yellowish, flammable powder or flakes with a pungent odor.
Representative
| Diphenylmethane diisocyanates | |||||
| Surname | Diphenylmethane 2,2'-diisocyanate |
Diphenylmethane 2,4'-diisocyanate |
Diphenylmethane 4,4'-diisocyanate |
||
| other names | 2,2'-Diphenylmethane diisocyanate 2,2'-MDI |
2,4'-Diphenylmethane diisocyanate 2,4'-MDI |
4,4'-diphenylmethane diisocyanate p , p '-diphenylmethane diisocyanate 4,4'-MDI |
||
|
Methylene |
|||||
| Structural formula |  |
 |

|
||
| CAS number | 2536-05-2 | 5873-54-1 | 101-68-8 | ||
| 26447-40-5 (mixture of isomers) 9016-87-9 (technical) |
|||||
| PubChem | 62450 | 62593 | 7570 | ||
| Molecular formula | C 15 H 10 N 2 O 2 | ||||
| Molar mass | 250.26 g mol −1 | ||||
| Physical state | firmly | ||||
| Brief description | colorless to yellowish, flammable powder or flakes with an amine-like, pungent odor | ||||
| Melting point | 40 ° C | 37 ° C | 40 ° C | ||
| boiling point | 300 ° C | ||||
| density | 1.18 g cm −3 | ||||
| solubility | Decomposes in water, soluble in organic solvents such as B. acetone, ethyl acetate, N -methylpyrrolidone and halogenated hydrocarbons |
||||
|
GHS labeling |
from Regulation (EC) No. 1272/2008 (CLP) , expanded if necessary
|
||||
| H-phrases | 351-332-373-319-335-315-334-317 | ||||
| EUH phrases | no EUH phrases | 204 | no EUH phrases | ||
| P-phrases | ? |
260-280-285-302 + 352-304 + 340- 305 + 351 + 338-309 + 311 |
261-280-284-304 + 340-312- 305 + 351 + 338-342 + 311 |
||
Extraction and presentation
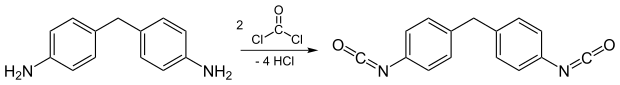
The production of MDI takes place in several stages. First, aniline is reacted with formaldehyde to form diaminodiphenylmethane :
The diaminodiphenylmethane is then reacted with phosgene to form diisocyanate.
properties
Depending on the position of the isocyanate groups, the isomers differ in their reactivity. The isocyanate groups in the 4-position are much more reactive than those in the 2-position.
use
Methylenedi (phenyl isocyanate) is an essential raw material for polyurethane , polyamide-imide and flexible foam, insulating foam and adhesives. It is therefore one of the most widely produced isocyanates in the world, along with TDI . In rare cases, technical diphenylmethane diisocyanate is also used to glue MDF boards .
Safety instructions / risk assessment
Methylenedi (phenyl isocyanate) can be easily brought to polymerisation by heat , which can be violent. Furthermore, the substance is classified as carcinogenic according to EC category 2 (substances that give cause for concern because of their possible carcinogenic effects in humans).
In 2012, 4,4'-methylenediphenyl diisocyanate was included in the EU's ongoing action plan ( CoRAP ) in accordance with Regulation (EC) No. 1907/2006 (REACH) as part of substance evaluation . The effects of the substance on human health and the environment are re-evaluated and, if necessary, follow-up measures are initiated. The reasons for the uptake of 4,4'-methylenediphenyl diisocyanate were concerns about its classification as a CMR substance, consumer use and widespread use, as well as the dangers arising from a possible assignment to the group of PBT / vPvB substances and the suspected dangers of sensitizing properties . The re-evaluation started in 2013 and was carried out by Estonia . A final report was then published.
See also
Web links
- News entry about the BASF plant in Antwerp with an annual production of 320,000 tons
- Methylene diphenyl diisocyanate (MDI) - overview DOW
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b Entry on diphenylmethane diisocyanate in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on August 11, 2016(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ a b c d e Entry on diphenylmethane-2,2′-diisocyanate in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on August 11, 2016(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ a b c d e f Entry on diphenylmethane-2,4′-diisocyanate in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on August 11, 2016(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ a b c d e f Entry on diphenylmethane-4,4′-diisocyanate in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on August 11, 2016(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ Data sheet 4,4′-MDI (PDF; 207 kB) at GisChem, accessed on May 7, 2018.
- ↑ Entry on Methylenediphenyl diisocyanate in the Classification and Labeling Inventory of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), accessed on August 11, 2016. Manufacturers or distributors can expand the harmonized classification and labeling .
- ↑ David Randall, Steve Lee: The Polyurethanes Book . Wiley, New York 2002, ISBN 0-470-85041-8 .
- ↑ European Chemicals Agency (ECHA): Substance Evaluation Conclusion and Evaluation Report .
- ↑ Community rolling action plan ( CoRAP ) of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA): 4,4'-methylenediphenyl diisocyanate , accessed on May 20, 2019.