Methylhexanamine
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
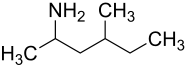
|
||||||||||||||||
| Structural formula without specifying the stereochemistry - mixture of stereoisomers | ||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Methylhexanamine | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 7 H 17 N | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
liquid |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 115.22 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
liquid |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
0.764 g cm −3 |
|||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
130-135 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| Refractive index |
1.417-1.419 (20 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . Refractive index: Na-D line , 20 ° C | ||||||||||||||||
Methylhexaneamine (better known as DMAA, for [1,3] Dimethylamylamine is) a substance from the group of amines , the nutritional supplements to improve athletic performance is illegally added - preferably in weight training to increase for a certain period -.
The substance was developed by the US Eli Lilly and Company and has been marketed since April 1944 as a component of the drug Forthane (indication: swelling of the nasal mucous membrane). In 1983 the indirect sympathomimetic was taken off the market.
Stereochemistry
Methylhexanamine contains two stereogenic centers and is usually a mixture of the following four isomeric chemical compounds :
- (2 R , 4 R ) -4-methyl-2-hexanamine
- (2 S , 4 S ) -4-methyl-2-hexanamine
- (2 S , 4 R ) -4-methyl-2-hexanamine
- (2 R , 4 S ) -4-methyl-2-hexanamine
It is generally known that stereoisomers - e.g. B. of drugs - usually have different physiological properties.
presentation
Methylhexanamine is synthetically accessible by reacting 4-methylhexan-2-one with hydroxylammonium chloride to form the oxime and subsequent reduction with sodium in ethanol .
Structural similarity to amphetamine
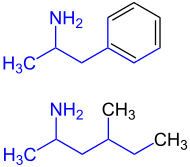
The similarities between the chemical structural formulas of amphetamine and methylhexanamine are striking. Amphetamine is widely used as an intoxicant because of its effects - suppressing tiredness and increasing self-confidence - the trade and possession of amphetamines without a permit is a criminal offense in Germany and most European countries.
As deaths occurred after taking methylhexanamine, this drug was banned from the European market. In the USA it was freely available as a dietary supplement in many products until the beginning of 2013 , for example as an ingredient in so-called “pre-workout drinks”. In April 2013, the FDA advised dietary supplement manufacturers that using methylhexanamine was illegal. At the same time, US consumers have been warned of the serious health risks associated with consuming products containing methylhexanamine.
doping
Food supplements contaminated with methylhexanamine lead to around 300 doping cases worldwide every year. At the Olympic Winter Games 2014 in Sochi on February 21, 2014, the German biathlete Evi Sachsenbacher-Stehle found methylhexanamine in a doping control in both the A and B samples. Regional league soccer player Cebio Soukou ( Rot-Weiss Essen ) tested positive for methylhexanamine on December 6, 2014. The player had subsequently assured himself that he could only explain the results of the doping test on the basis of unspecified and accordingly illegal additives in a food supplement he had taken. An appraiser confirmed the player's statements. Soukou was banned for 5 months anyway and 1 point was deducted from the club.
DMAA is named as a substance prohibited in competition in NADA's 2018 Prohibited List under p. 6 ( stimulants ).
Analytical evidence
A validated analytical method for the detection of 4-methyl-2-hexanamine in food supplements and in human urine is known. After taking 40 mg , 350 ng / ml could be detected in the urine after up to four days.
Web links
- dopinginfo.de: methylhexanamine
- Beware of dietary supplements. National Anti Doping Agency Germany (NADA), February 19, 2016, accessed on March 9, 2016 : "Dietary supplements may contain prohibited substances such as higenamine, methylhexanamine, oxilofrin or sibutramine."
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g data sheet 1,3-Dimethylamylamine, analytical standard from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on May 13, 2017 ( PDF ).
- ^ EJ Ariëns: Stereochemistry, a basis for sophisticated nonsense in pharmacokinetics and clinical pharmacology . In: Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. . 26 , No. 6, 1984, pp. 663-668. PMID 6092093 .
- ↑ Entry on 1,3-dimethylamylamine. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on August 1, 2018.
- ↑ a b Natasha Singer, Peter Lattman: FDA Issues Warning on Workout Supplement . In: New York Times , April 16, 2013.
- ^ Stimulant Potentially Dangerous to Health, FDA Warns . US Food and Drug Administration . April 16, 2013. Retrieved April 16, 2013.
- ↑ Analyst Geyer: "Simply stupid" . Daily mirror . July 17, 2013. Retrieved February 21, 2014.
- ↑ dosb.de: NADA statement on the doping case "Methylhexanamine" in Sochi , February 21, 2014.
- ↑ Sachsenbacher-Stehle confirms positive doping test . The mirror . February 21, 2014. Retrieved February 21, 2014.
- ↑ Point deduction for Rot-Weiss Essen . FuPa. January 30, 2015. Accessed January 30, 2015.
- ↑ Laurent Perrenoud, Martial Saugy, Christophe Saudan: Detection in urine of 4-methyl-2-hexaneamine, a doping agent , Journal of Chromatography B 877 (2009) pp. 3767-3770, doi : 10.1016 / j.jchromb.2009.09. 013 .



