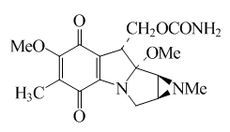
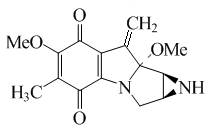
Mitomycins
The mitomycins are a group of aziridine- containing natural substances that can be formed by the actinobacteria Streptomyces caespitosus or Streptomyces lavendulae from the genus Streptomyces and isolated therefrom. The common structural element of the mitomycins is the mitosan chromophore .
history
Mitomycins A and B were first isolated from Streptomyces caespitosus in 1956 by Ryozo Sugawara and Toju Hata . Mitomycin C, which was initially called mitomycin X , could still be separated from the two main fractions in 1958 .
description
The pharmacologically important mitomycins are mitomycin A , mitomycin B , mitomycin C and mitomycin D . Of all the mitomycins, mitomycin C is by far the most important. It is currently the only approved chemotherapeutic agent from the mitomycin group. It is often called just mitomycin .
Of the 17 natural mitomycins known in 2009, 16 are biologically active in that they have either antibiotic or cytostatic properties.
| structure | Surname | Molecular formula | CAS number | Molar mass [g / mol] | source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mitomycin A | C 16 H 19 N 3 O 6 | 4055-39-4 | 349,343 | ||
| Mitomycin B | C 16 H 19 N 3 O 6 | 4055-40-7 | 349,343 | ||
| Mitomycin C | C 15 H 18 N 4 O 5 | 50-07-7 | 334,331 | ||
| Mitomycin D | C 15 H 18 N 4 O 5 | 10169-34-3 | 334,331 | ||
| Mitomycin E. | C 16 H 20 N 4 O 5 | 74707-94-1 | 348,358 | ||
| Mitomycin F | C 17 H 21 N 3 O 6 | 18209-14-8 | 363,369 | ||
| Mitomycin J. | C 17 H 21 N 3 O 6 | 74985-82-3 | 363,369 | ||
| Mitomycin K | C 16 H 18 N 2 O 4 | 74148-45-1 | 302,329 |
Such as:
- Mitomycin G, CAS number 74148-46-2
- Mitomycin H, CAS number 74148-44-0
biosynthesis
The biosynthesis in the two Streptomyces species takes place via three building blocks 3-amino-5-hydroxybenzoic acid (AHBA), D - glucosamine and carbamoyl phosphate .
AHBA is built up enzymatically in several stages from phosphoenolpyruvic acid (PEP) and erythrose-4-phosphate (E4P).
Total synthesis
The total synthesis of the mitomycins is extremely demanding. The American chemist Samuel Danishefsky said:
"The synthesis of a mitomycin is the chemical equivalent of walking on egg shells."
In German, for example: "The synthesis of a mitomycin is the chemical equivalent of an egg dance".
In his twelve-step synthesis of mitomycin K published in 1992, Danishefsky came up with an overall yield of 0.3%. In the first total synthesis of mitomycin A and C carried out in the late 1970s, Yoshito Kishi required 45 and 46 steps, respectively, and an overall yield was 0.05%. However, the average yield per stage was 84%.
literature
- KR Kunz, BS Iyengar u. a .: Structure-activity relationships for mitomycin C and mitomycin A analogues. In: Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. Volume 34, Number 7, July 1991, pp. 2281-2286, PMID 1906109 .
- N. Sitachitta, NB Lopanik a. a .: Analysis of a parallel branch in the mitomycin biosynthetic pathway involving the mitN-encoded aziridine N-methyltransferase. In: The Journal of biological chemistry. Volume 282, Number 29, July 2007, pp. 20941-20947, doi: 10.1074 / jbc.M702456200 , PMID 17507379 .
- DA Gubler, RM Williams: Synthetic Studies Towards the Mitomycins: Construction of the Tetracyclic Core via a Reductive Aminocyclization Reaction. In: Tetrahedron letters. Volume 50, number 29, July 2009, pp. 4265-4267, doi: 10.1016 / j.tetlet.2009.05.004 , PMID 20161278 , PMC 2702872 (free full text).
- Entry to Mitomycins. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on May 4, 2015.
Individual evidence
- ↑ Helga Kersten, Walter Kersten: On the mode of action of Mitomycin C, II. Influence of Mitomycin C, Chloramphenicol and Mg 2+ on the RNA and DNA metabolism in bacteria. In: Hoppe-Seyler's magazine for physiological chemistry. 334, 1963, p. 141, doi: 10.1515 / bchm2.1963.334.1.141 .
- ↑ Hans-J. Rehm: Introduction to Industrial Microbiology. Springer-Verlag, 2013, ISBN 978-3-642-65072-7 , p. 179 ( limited preview in the Google book search).
- ↑ T. Hata, R. Sugawara: Mitomycin, a new antibiotic from Streptomyces. II. Description of the strain. In: The Journal of antibiotics. Volume 9, Number 4, July 1956, pp. 147-151, PMID 13385187 .
- ↑ T. Hata, T. Hoshi et al. a .: Mitomycin, a new antibiotic from Streptomyces. I. In: The Journal of Antibiotics. Volume 9, Number 4, July 1956, pp. 141-146, PMID 13385186 .
- ↑ The pathophysiology and the pathomechanism: results of internal medicine and paediatrics . 1963 ( limited preview in Google Book Search).
- ^ Maki Umemura: The Japanese Pharmaceutical Industry. Taylor & Francis, 2011, ISBN 978-1-136-82825-6 , p. 143 ( limited preview in Google book search).
- ↑ SM Sami, WA Remers, WT Bradner: Preparation and antitumor activity of additional mitomycin A analogues. In: Journal of Medicinal Chemistry . Volume 32, Number 3, March 1989, pp. 703-708, PMID 2918519 .
- ↑ JH Beijnen, OA van der Houwen u. a .: A systematic study on the chemical stability of mitomycin A and mitomycin B. In: Chemical & pharmaceutical bulletin. Volume 34, Number 7, July 1986, pp. 2900-2913, PMID 3769091 .
- ↑ L. Kahmann, U. Beyer u. a .: Mitomycin C in patients with gynecological malignancies. In: Oncology. Volume 33, number 10, 2010, pp. 547-557, doi: 10.1159 / 000319742 , PMID 20926904 .
- ↑ A. Volpe, M. Racioppi et al. a .: Mitomycin C for the treatment of bladder cancer. In: Minerva urologica e nefrologica = The Italian journal of urology and nephrology. Volume 62, Number 2, June 2010, pp. 133-144, PMID 20562793 .
- ↑ a b N. Hirayama, H. Arai, M. Kasai: Structural studies of mitomycins. VIII. Mitomycin D hydrate, C15H18N4O5.1.5H2O. In: Acta crystallographica. Section C, Crystal structure communications. Vol. 52 (Pt 9), September 1996, pp. 2365-2367, PMID 8828157 .
- ↑ a b c Rockford Coscia: Mitomycin - Molecule in Review. ( Memento of the original from June 26, 2010 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. Columbia University Chemistry, (PDF file).
- ↑ MITOMYCIN A - National Library of Medicine HSDB Database. In: toxnet.nlm.nih.gov. Retrieved May 4, 2015 .
- ↑ MITOMYCIN B - National Library of Medicine HSDB Database. In: toxnet.nlm.nih.gov. Retrieved May 4, 2015 .
- ↑ MITOMYCIN C - National Library of Medicine HSDB Database. In: toxnet.nlm.nih.gov. Retrieved May 4, 2015 .
- ^ Entry on mitomycins in the ChemIDplus database of the United States National Library of Medicine (NLM), accessed on May 4, 2015.
- ↑ External identifiers or database links for Mitomycin E : CAS number: 74707-94-1, PubChem : 3058219 , ChemSpider : 2319381 , Wikidata : Q27255534 .
- ↑ N. Sitachitta, NB Lopanik a. a .: Analysis of a parallel branch in the mitomycin biosynthetic pathway involving the mitN-encoded aziridine N-methyltransferase. In: The Journal of biological chemistry. Volume 282, Number 29, July 2007, pp. 20941-20947, doi: 10.1074 / jbc.M702456200 , PMID 17507379 .
- ↑ John W. Benbow, Gayle K. Schulte, Samuel J. Danishefsky: The Total Synthesis of (±) -Mitomycin K. In: Angewandte Chemie International Edition in English. 31, 1992, p. 915, doi: 10.1002 / anie.199209151 .
- ↑ Tohru Fukuyama, Lihu Yang: Practical total synthesis of (±) -mitomycin C. In: Journal of the American Chemical Society. 111, 1989, p. 8303, doi: 10.1021 / ja00203a055 .
- ↑ N. Hirayama, H. Arai, M. Kasai: Structural studies of mitomycins. VII. Mitomycin G. In: Acta crystallographica. Section C, Crystal structure communications. Vol. 52 (Pt 7), July 1996, pp. 1806-1808, PMID 8756264 .
- ↑ N. Hirayama: Structural studies of mitomycins. V. Structure of mitomycin H. In: Acta Crystallographica Section C Crystal Structure Communications. 47, p. 604, doi: 10.1107 / S0108270190007235 .
- ↑ HG Floss, TW Yu, K. Arakawa: The biosynthesis of 3-amino-5-hydroxybenzoic acid (AHBA), the precursor of mC7N units in ansamycin and mitomycin antibiotics: a review. In: The Journal of antibiotics. Volume 64, number 1, January 2011, pp. 35-44, doi: 10.1038 / ja.2010.139 , PMID 21081954 .
- ↑ a b Jeremy May, Dan Caspi, Neil Garg include: Synthetic Enchantment with Mitomycinoids. ( Memento of the original from June 24, 2010 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. 16 August 2004.
- ^ Yoshito Kishi: The Total Synthesis of Mitomycins. In: Journal of Natural Products. 42, 1979, p. 549, doi: 10.1021 / np50006a001 .