Nickel oxalate
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
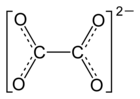
|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Nickel oxalate | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
Nickel (II) oxalate |
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | NiC 2 O 4 | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
green-white solid |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 146.70 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
|
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Nickel oxalate is a chemical compound of nickel from the group of carboxylic acid salts .
Extraction and presentation
Nickel oxalate can be obtained by reacting nickel (II) salt solutions with oxalic acid , or better an alkali metal oxalate, resulting in the dihydrate.
properties
As a dihydrate, nickel oxalate is a greenish-white solid that is practically insoluble in water. It occurs in two different crystal structures . The metastable β-form has an orthorhombic crystal structure, the α-form has a monoclinic crystal structure. By heating these can be converted into the anhydrate from around 150 ° C, whereby the release of crystal water is not complete. From around 280 ° C this decomposes to nickel, nickel (II) oxide and mainly carbon dioxide . Like other metal oxalate anhydrates, β-MeC 2 O 4, the anhydrate has a monoclinic crystal structure with the space group P 2 1 / n (space group no. 14, position 2) .
use
Nickel oxalate is used as an intermediate product in the production of nickel and nickel (II) oxide (e.g. from ores and for recycling batteries).
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e William M. Haynes: CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, 94th Edition . CRC Press, 2016, ISBN 978-1-4665-7115-0 , pp. 78 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ Entry on nickel oxalate in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on July 23, 2016(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ Entry on nickel oxalate in the Classification and Labeling Inventory of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), accessed on August 1, 2016. Manufacturers or distributors can expand the harmonized classification and labeling .
- ↑ Data sheet Nickel (II) oxalate dihydrate, 99.999% trace metals basis from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on June 27, 2016 ( PDF ).
- ↑ a b Wolfgang Hummel: Chemical Thermodynamics of Compounds and Complexes of U, Np, Pu, Am, Tc, Se, Ni and Zr With Selected Organic Ligands . Elsevier, 2005, ISBN 978-0-08-045752-9 , pp. 190 ( limited preview in Google Book Search).
- ^ Ronald Rich: Inorganic Reactions in Water . Springer, 2007, ISBN 978-3-540-73962-3 , pp. 243 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ B. Małecka, A. Małecki, E. Drożdż-Cieśla, L. Tortet, P. Llewellyn, F. Rouquerol: Some aspects of thermal decomposition of NiC2O4 · 2H2O . In: Thermochimica Acta . tape 466 , no. 1–2 , December 30, 2007, pp. 57-62 , doi : 10.1016 / j.tca.2007.10.010 ( sciencedirect.com ).
- ^ B. Delmon, P. Grange, PA Jacobs, G. Poncelet: Preparation of Catalysts V Scientific Bases for the Preparation of Heterogeneous Catalysts . Elsevier, 1991, ISBN 978-0-08-087919-2 , pp. 172 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ Boris V. L'vov: Thermal Decomposition of Solids and Melts New Thermochemical Approach to the Mechanism, Kinetics and Methodology . Springer Science & Business Media, 2007, ISBN 978-1-4020-5672-7 , pp. 223 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ Xiao Ming Fu, Zai Zhi Yang: Preparation of Spherical NiO Nanoparticles by the Thermal Decomposition of NiC 2 O 4 2H 2 O Precursor in the Air. In: Advanced Materials Research. 228-229, 2011, p. 34, doi : 10.4028 / www.scientific.net / AMR.228-229.34 .
- ↑ B.-R. Shen, H. Shen, Y.-X. Pan, T.-F. Chen, X.-E. Cai: The Thermal Decomposition of NiC2O4 · 2H2O: An In Situ TP-XRD and TGA / FT-IR Study . In: Journal of Physical Chemistry . tape 215 , no. 11/2001 , January 1, 2001, ISSN 0942-9352 , doi : 10.1524 / zpch.2001.215.11.1413 ( researchgate.net ).
- ↑ Andrzej Koleżyński, Bartosz Handke, Ewa Drożdż-Cieśla: Crystal structure, electronic structure, and bonding properties of anhydrous nickel oxalate. In: Journal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry. 113, 2013, p. 319, doi : 10.1007 / s10973-012-2844-y .
- ↑ Nagaiyar Krishnamurthy, Chiranjib Kumar Gupta: Extractive Metallurgy of Rare Earths, Second Edition . CRC Press, 2015, ISBN 978-1-4665-7638-4 , pp. 665 ( limited preview in Google Book search).



