Oxaliplatin
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
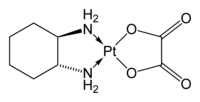
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Non-proprietary name | Oxaliplatin | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 8 H 14 N 2 O 4 Pt | ||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Drug information | |||||||||||||||||||
| ATC code | |||||||||||||||||||
| Drug class | |||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 397.28 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | |||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||||||||
Oxaliplatin is a cytostatically active drug from the group of platinum derivatives. It is approved in combination with 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) and folinic acid (FS) for the treatment of colorectal cancer ( FOLFOX scheme).
chemistry
Oxaliplatin is an antineoplastic substance and belongs to a new class of platinum complexes in which the platinum ion is complexed with a 1,2-diaminocyclohexane ligand ( DACH ligand for short) and an oxalate ion. Oxaliplatin is a pure enantiomer , the cis - [oxalato ( trans - L -1,2-diaminocyclohexane) platinum].
pharmacology
effectiveness
The effectiveness of the combination therapy of oxaliplatin with 5-fluorouracil / folinic acid (5-FU / FS) has been proven in numerous studies . Oxaliplatin is included in all guidelines for the treatment of colorectal cancer for the respective indication areas with the highest level of recommendation. Current studies indicate that an additional combination with the monoclonal antibody bevacizumab or panitumumab can further improve survival rates significantly.
application
Oxaliplatin is used in combination with 5-fluorouracil and folinic acid and is approved for adults
- for the adjuvant treatment of stage III colon cancer (Dukes C) after complete removal of the primary tumor,
- for the treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer.
A common combination is the FOLFOX4 regimen with an oxaliplatin infusion on the first day and subsequent continuous infusion of 5-fluorouracil over two days.
Mechanism of action
Oxaliplatin has the effect that metabolic products formed in the body, similar to cis- or carboplatin, interact with the DNA and form cross-links in and between the DNA strands. The 1,2-diaminocyclohexane ligand (DACH ligand) influences the ability of the cell to tolerate DNA-platinum adducts. The difference in the effect of oxaliplatin and cis- / carboplatin is based on this. The DACH-platinum adducts, which are formed from oxaliplatinum, inhibit DNA synthesis more strongly than the cis-diamino-platinum adducts, which are formed from cis- and carboplatinum.
Side effects
The most common side effects of oxaliplatin in combination with 5-fluorouracil and folinic acid are diarrhea , nausea, vomiting and inflammation of the mucous membranes, changes in the blood count and peripheral sensory neuropathy (s) (neurological abnormalities). The latter is often dose-limiting.
development
- 1996 - Oxaliplatin approved for second line treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer in France
- 1998 - Approval extension also for first line therapy
- 1999 - Approval of oxaliplatin for first line therapy as part of the mutual recognition process in Germany and the other European countries
- 2002 - FDA approved oxaliplatin for second-line treatment of advanced colorectal cancer in the US
- 2004 - Approval extensions also for first line therapy in the USA and for the adjuvant treatment of colon cancer in the early stages in Europe
Trade names
Bendaplatin (D), Croloxat (D), Eloxatin (D, A, CH), Medoxa (D), various generics (D, A)
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b Oxaliplatin data sheet from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on April 16, 2011 ( PDF ).
- ↑ Entry on oxaliplatin in the ChemIDplus database of the United States National Library of Medicine (NLM)