Pancreatic amylase
| Pancreatic amylase | ||
|---|---|---|
|
||
|
Existing structural data: see UniProt |
||
| Properties of human protein | ||
| Secondary to quaternary structure | Monomer | |
| Cofactor | Calcium, chloride | |
| Identifier | ||
| Gene names | AMY2A , AMY2B ; AMYP; PA | |
| External IDs | ||
| Drug information | ||
| DrugBank | DB00085 | |
| Drug class | Enzyme replacement | |
| Enzyme classification | ||
| EC, category | 3.2.1.1 , glycosidase | |
| Response type | Hydrolysis of 1,4-α-D-glycoside bonds | |
| Substrate | Starch, glycogen and similar oligo- or polysaccharides | |
| Products | Mono-, oligosaccharides | |
| Occurrence | ||
| Homology family | Glycosidase | |
| Parent taxon | Creature | |
| Orthologue | ||
| human | House mouse | |
| Entrez | 279 | 11722 |
| Ensemble | ENSG00000243480 | ENSMUSG00000074264 |
| UniProt | P04746 | P00687 |
| Refseq (mRNA) | NM_000699 | NM_001110505 |
| Refseq (protein) | NP_000690 | NP_001103975 |
| Gene locus | Chr 1: 103.62 - 103.63 Mb | Chr 3: 113.56 - 113.61 Mb |
| PubMed search | 279 |
11722
|
With pancreatic amylase (Amy2, Amy-P) two isoforms of human α- be amylase refers to that enzyme , the polysaccharides such as starch into smaller oligosaccharides such as maltose hydrolyzed (split). The pancreatic amylase is produced in the acinar cells of the pancreas and released into the digestive tract. Normally only a small part of this enzyme gets into the blood. The genes for the two isoforms are called AMY2A and AMY2B . The other three isoforms of the enzyme are called salivary amylase .
Catalyzed reaction
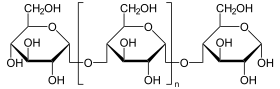 (n large) ⇒
(n large) ⇒
⇒  (n small) +
(n small) +
+  (n small) + ...
(n small) + ...
Poly-D-glucose is crushed until only maltose and maltotriose are left. The enzyme is also able to deal with 1-6 branched sugar chains ( amylopectin ); the additional end products are limit dextrins .
Laboratory diagnostics
In laboratory diagnostics, the activity of pancreatic amylase from heparin plasma or blood serum is measured in the clarification of upper abdominal pain, especially for the diagnosis of acute pancreatitis .
The determination of pancreatic amylase in chronic pancreatitis and pancreatic tumors is not very sensitive; H. the value is often below the reference range despite the illness.
Preanalytics
The enzyme needs calcium for its function. EDTA plasma or citrate plasma are therefore not suitable for the determination. The enzyme is stable for four days in whole blood and one week in plasma. The samples can be kept for one year at −20 ° C. With the current test methods, about 3% salivary amylase is also determined. These can be found in saliva and sweat, with which the sample material must not be contaminated under any circumstances.
Reference range for measurements at 37 ° C according to IFCC
| Serum, plasma | <53 U / l |
interpretation
In acute pancreatitis , the pancreatic amylase increases to over 150 U / l 2-12 hours after the onset of pain. The plasma half-life is 9-18 hours, i.e. H. After just 1-2 days, the activity in the plasma falls again below the reference range of 53 U / l.
Remarks
There is no relationship between the severity of the disease and the level of enzyme activity in the plasma. The determination is therefore only suitable for diagnosis, but not for the course or prognosis.
The mass of the enzyme is only 50 kDa . It is the only enzyme in laboratory diagnostics that is excreted via the kidneys and can therefore also be determined in the urine. Correspondingly, increased values are found in renal insufficiency .
So-called macroamylase is found in up to three percent of the population, which due to its size is not excreted renally and therefore causes an increase in amylase in the plasma without pancreatic disease. This form of amylase is harmless, but it can make the laboratory results difficult to interpret. Increased pancreatic amylase in the blood with normal pancreatic amylase in the urine suggests macroamylase. Gullo syndrome can be another cause of increased amylase without a disease value .
When using plasma expanders with hydroxyethyl starch, large complexes of amylase and the polysaccharide are also formed, which leads to an increase in amylase activity.
When using plasma expanders with Dextran 70, the test may give too low results. In such cases the lipase has to be determined.
literature
- Neumeister, Besenthal, Liebrich: Clinical guidelines for laboratory diagnostics. Urban & Fischer, Munich / Jena 2003, ISBN 3-437-22231-7 .
- Lothar Thomas: Laboratory and Diagnosis. TH-Books, Frankfurt am Main 2005, ISBN 3-9805215-5-9 .
Web links
- alpha-amylase. med4you.at
- Approved Recommendation on IFCC Methods for the Measurement of Catalytic Concentration of Enzymes Part 9.IFCC Method for a-Amylase (1,4-aD-Glucan 4-Glucanohydrolase, EC 3.2.1.1) ( Memento of January 18, 2004 in the Internet Archive ; PDF) In: Clin Chem Lab Med , 1998, 36 (3), pp. 185-203
- Stability in blood samples (PDF; 292 kB) published by the WHO
Individual evidence
- ^ D'Eustachio, Nichols: Digestion of linear starch (amylose) by extracellular amylase . reactome.org
- ↑ D'Eustachio, Nichols: Digestion of branched starch (amylopectin) by extracellular amylase . reactome.org