Parkfield
| Parkfield | ||
|---|---|---|
|
Location in California
|
||
| Basic data | ||
| State : | United States | |
| State : | California | |
| County : | Monterey County | |
| Coordinates : | 35 ° 54 ′ N , 120 ° 26 ′ W | |
| Time zone : | Pacific ( UTC − 8 / −7 ) | |
| Residents : | 900 (as of:) | |
| Height : | 466 m | |
| Postal code : | 93451 | |
| Area code : | +1 805 | |
| FIPS : | 06-55716 | |
| GNIS ID : | 1661195 | |
 Position of the village of Parkfield |
||
Parkfield is a scattered rural settlement in the US state of California ( Monterey County ), halfway between Los Angeles and San Francisco . The approximately 900 inhabitants live mainly from agriculture, mainly from cattle breeding, and some tourism.
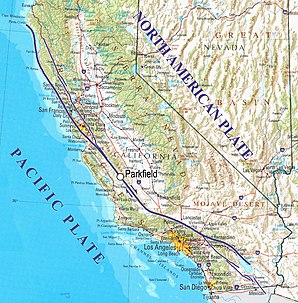
Parkfield's specialty lies in the fact that it lies directly on the San Andreas Fault , one of the longest and most geologically active zones in the world. The epicenter of the Fort Tejon earthquake in 1857 , one of the most severe earthquakes in California, was near this location. Parkfield has an earthquake of magnitude six or greater every 22 years on average. The American federal authority United States Geological Survey predicted a major quake in 1993 in the 1985th However, this did not occur until September 28, 2004, when a magnitude six earthquake occurred around ten in the morning.
Parkfield is one of the regions in the world that are most closely observed due to its seismic hazard. In seismology , monitoring by the United States Geological Survey is known as the Parkfield Experiment . The aim of the research is to improve the prediction of earthquakes. The center of the field station is a measuring field made up of pegs, laid out in lines in 1969, moved across the plate boundary and filmed around the clock in order to be able to detect sudden jumps caused by earthquakes. Tensions in the ground can be determined using 15 wire measuring devices. The station also measures modifications of the frequency amplitude of emitted microwaves with the aid of satellites. A laser can also be used to measure the distance to several reflectors permanently installed in the landscape. In addition, the concentrations of the radioactive noble gas radon , which increasingly enters the atmosphere during earthquakes, are regularly determined.