Phenyl magnesium bromide
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Phenyl magnesium bromide | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
Bromine (phenyl) magnesium |
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 6 H 5 BrMg | |||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 181.31 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Phenylmagnesium bromide is a chemical compound from the group of benzene derivatives and organometallic compounds . As a Grignard reagent , it is usually only stable as a solvent adduct with two equivalents of an ether .
Extraction and presentation
To obtain phenylmagnesium bromide, bromobenzene is slowly added to magnesium turnings in dry ether . As soon as the reaction has started successfully, the ether turns gray-violet and the solution heats up to boiling if the aromatic compound is added more quickly. The reaction can be strongly inhibited by the always existing oxide layer on the magnesium, which is why it is often etched beforehand by adding a few iodine crystals. Phenylmagnesium bromide, like all Grignard reagents, is normally not isolated but used in solution.
Due to their high reactivity, it is necessary when working with phenylmagnesium bromide solutions to strictly exclude water - by using a drying tube and chemically dried ( "ketylated" ) solvents - otherwise benzene and magnesium hydroxide precipitating in the ether will form. Phenylmagnesium bromide is mostly generated in situ and, due to its sensitivity to (air) moisture and - due to its instability to acids - carbon dioxide contained in the air, it is not stored for long. As with all aromatic Grignard compounds, tetrahydrofuran (THF) is preferable to diethyl ether as a solvent because of its better stabilization and thus the reactivity it enables.
properties
As a so-called Grignard reagent, phenylmagnesium bromide is an important chemical in organic chemistry, at the same time a strong base and is used in Grignard reactions to form new carbon-carbon single bonds.
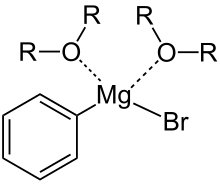
Usually it is not isolated as a free substance, but only used as a solution. The stability of the solutions of Grignard compounds is based on the coordination of the lone pairs of electrons of the oxygen atom contained in the ether. Since the butylene group in THF is "fixed" (sterically inhibited) by its ring-shaped structure and is not freely mobile like the ethyl groups in diethyl ether, the representation of sterically demanding Grignard compounds, such as (substituted) phenyl or benzyl halides, explains higher stability of the complex in THF, which applies analogously to other intramolecular ethers such as 1,4-dioxane and can be explained with the Schlenk equilibrium . The technical product for laboratory purposes is usually sold as a one, two or three molar solution in tetrahydrofuran or diethyl ether; Due to the low boiling point of the diethyl ether, however, the THF-based solutions are preferred in order to allow greater flexibility in the range of the reaction temperature.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b Datasheet Phenylmagnesium bromide solution from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on October 22, 2016 ( PDF ).
- ↑ Eberhard Breitmaier, Günther Jung; Organic chemistry; ISBN 978-3-13-541505-5 .
- ↑ Entry on Phenylmagnesium Bromide (16% in tetrahydrofuran, approx. 1 mol / L) at TCI Europe, accessed on November 12, 2017.


